Imagine you’re building a software product with a globally distributed team. Code flies back and forth, features evolve daily, and keeping track of changes becomes chaotic. Enter GitHub—a platform that has revolutionized how developers collaborate and manage code. But GitHub is more than just a repository; it’s a hub for project management, time tracking integrations, and cutting-edge tools like GitHub Copilot. This guide demystifies GitHub, explains how it works, covers key concepts like pull requests, compares alternatives, time tracking in GitHub, and shows how tools like Everhour can enhance productivity.
Overview: What Is GitHub?
GitHub is a web-based platform built on Git, an open-source version control system. Git tracks changes to code, enabling developers to collaborate without overwriting each other’s work. GitHub provides a user-friendly interface for hosting Git repositories, allowing teams to store code, manage issues, review changes, and collaborate on software projects.
Key aspects of GitHub
- Version control: Tracks file changes, enabling rollbacks and branch management.
- Collaboration: Supports multiple contributors working on the same project concurrently.
- Hosting: Provides cloud hosting for code repositories, eliminating the need for local servers.
- Community: Millions of developers share open-source projects, learn from each other, and contribute to shared codebases.
GitHub’s user base spans individuals, start-ups, and Fortune 500 companies. The platform is accessible via a web browser and can be integrated with IDEs, continuous integration systems, and countless developer tools.
Why Use GitHub?
- 🔀 Simplified collaboration: Branches let developers work independently; pull requests make merging safe.
- 🧐 Code review: Inline comments and discussions catch bugs and improve quality.
- ✅ Issue tracking: Built-in issues and boards manage tasks and progress.
- 🔗 Integrations: Connect with CI/CD tools, Slack, project management, and time tracking.
- 🌍 Open source community: Host or contribute to projects and share knowledge.
- 🔒 Security & compliance: Enterprise features include SAML SSO, audit logs, and detailed access controls.
Understanding GitHub’s Key Concepts
Git
Git is a distributed version control system created by Linus Torvalds in 2005. It allows multiple developers to track changes, branch off to experiment, and merge code safely. Without Git, teams could easily lose work or overwrite each other’s changes. GitHub builds on Git by adding cloud hosting, a user interface, and collaboration features. Learn the differences between Git vs GitHub here.
Repositories
A repository (repo) is a storage space for your project’s files. It contains code, documentation, and the entire history of changes. Repos can be public (accessible to everyone) or private (restricted to invited collaborators).
Learn how to delete a repository in GitHub here!
Branches
Branches allow developers to create copies of the codebase to work on features or fixes without affecting the main branch (often called main or master). When work is complete, branches can be merged back into the main branch.
Pull requests (PRs)
A pull request is a request to merge changes from one branch into another. It’s the cornerstone of collaboration on GitHub. PRs allow team members to review code, discuss changes, suggest improvements, and approve merges. PRs also enable automatic checks like unit tests and linting via continuous integration (CI) tools.
Why pull requests matter
- Ensure code quality through peer review.
- Provide documentation of changes and discussions.
- Trigger automated tests and checks.
- Facilitate knowledge sharing within a team.
Issues
Issues are GitHub’s built-in way to track bugs, tasks, questions or feature requests. Users can tag issues, assign them to team members, add labels (e.g., bug, enhancement, documentation), and connect them to pull requests. It issues can form part of project management workflows.
Learn about all the best bug trackers out there!
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a CI/CD service that automates workflows directly within GitHub. It can run tests, deploy code, automate issue triaging, and perform routine tasks based on events like PRs or pushes (learn how to push to GitHub here). Actions are defined in YAML files in the repo.
GitHub Copilot
GitHub Copilot is an AI-powered coding assistant developed by GitHub and OpenAI. It uses machine learning to suggest code snippets and entire functions in real time. Copilot can interpret context from comments and code to predict what you’re trying to build.
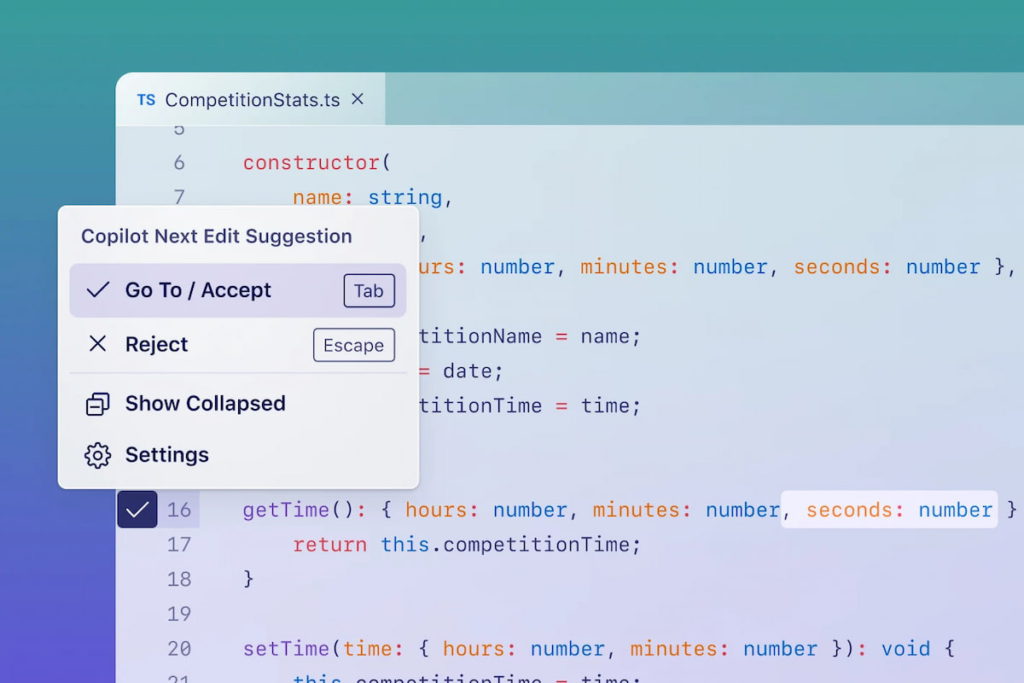
How Copilot works
- 🧠 Context-aware: Analyzes current code and comments to generate relevant suggestions.
- 💻 Programming language support: Works with Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, Go, Ruby, and more.
- 📘 Learning tool: Helps new developers understand patterns, learn libraries, and avoid repetitive typing.
- ⚠️ Limitations: Needs review to ensure quality; may suggest incorrect or insecure code.
GitHub Project Management
GitHub isn’t just for code storage. It offers features that rival standalone project management tools.
GitHub issues & labels
- Creation & assignment: Create issues for tasks, bugs, or feature requests. Assign to team members.
- Labels: Categorize issues by type, priority, or department (e.g., backend, urgent).
- Milestones: Group issues into milestones (e.g., v1.0 release) with deadlines.
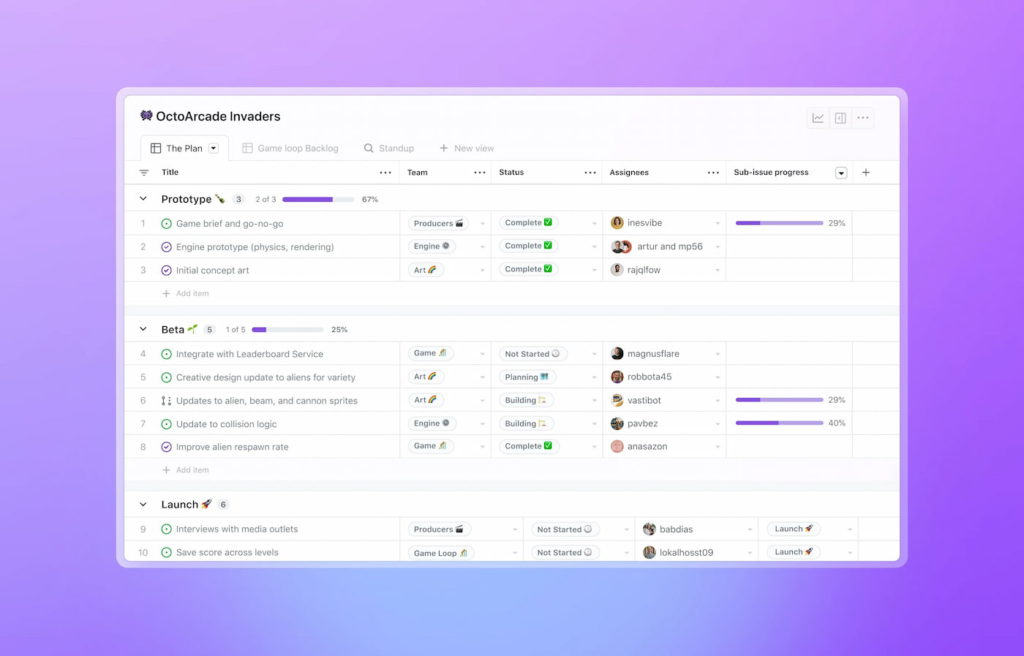
GitHub projects (Kanban boards)
GitHub Projects provides visual boards similar to Trello or Jira. Use them to plan and track work:
- Columns: Create columns like “To Do,” “In Progress,” “Done.”
- Cards: Add issues and PRs as cards. Drag them between columns.
- Automation: Automatically move cards based on actions (e.g., PR merged).
- Custom fields: Add deadlines, priorities or resource estimates.
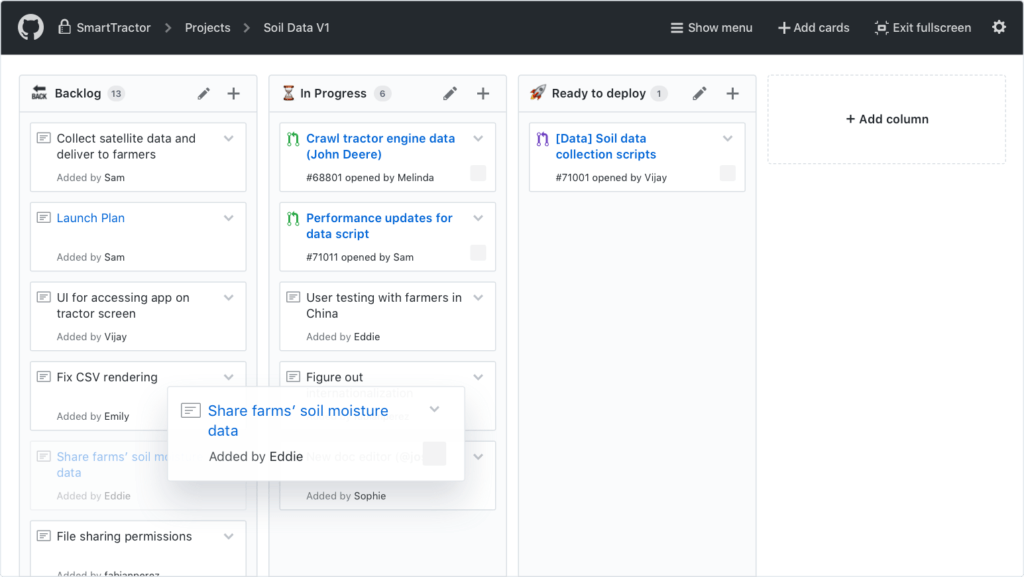
GitHub Time Tracking
GitHub doesn’t natively track time spent on tasks. To monitor hours, teams rely on integrations with time tracking tools. Time tracking is essential for:
- Client billing: Agencies and freelancers need to track billable hours.
- Project budgeting: Compare estimates vs actual effort.
- Resource planning: Understand team utilization and allocate work evenly.
Time tracking integrations
Several time tracking tools integrate with GitHub:
- Everhour: Add timers to GitHub issues or pull requests via browser extensions. Record time, set budgets and generate reports. Everhour links tracked time to specific tasks and clients, making billing and budgeting straightforward.
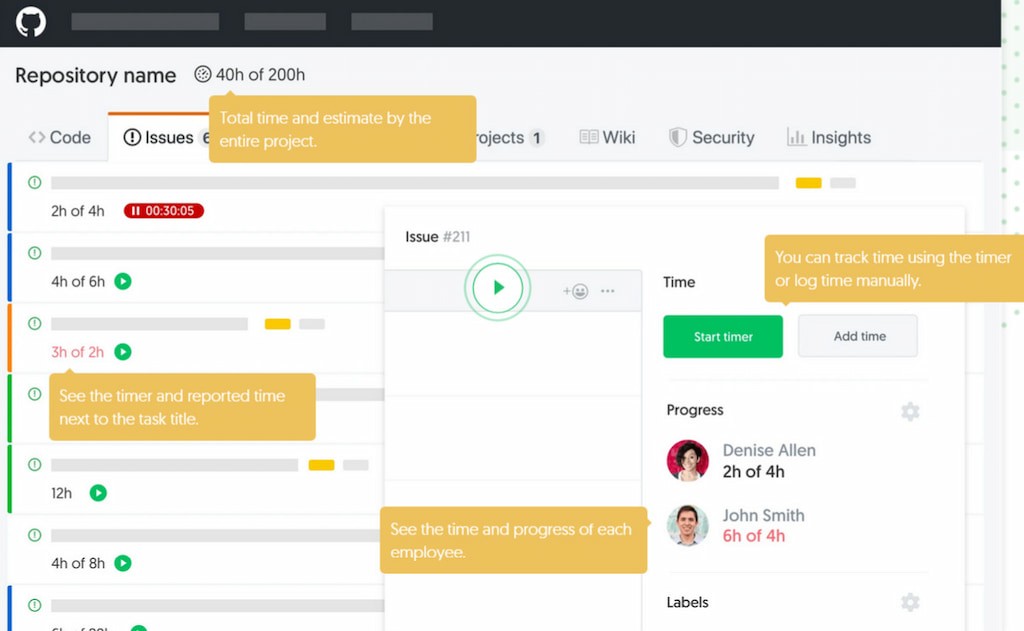
- Harvest: Users track time with browser extension or API integration. It logs time per issue and client.
- Toggl Track: Chrome extension allows starting/stopping timers in GitHub. Entries sync to Toggl.
Why Everhour fits
- ⏱️ Embedded in workflow: Timer appears directly on GitHub issues and PRs—no switching tools.
- 🚨 Budget alerts: Set time budgets per issue or project; get notified when limits are reached.
- 📊 Advanced reporting: Reports by issue, contributor, or client; integrates with QuickBooks/Xero for invoicing.
- 🔒 Privacy & simplicity: No screen or website monitoring—focuses only on logged hours.
- 🤝 Flexible teams: Works well for agencies, product teams, and freelancers using GitHub.
Example use case
A web development agency tracks tasks in GitHub Projects. With Everhour, designers and developers log time directly on issues. Weekly reports show hours per client project, enabling accurate billing and better task estimates.
GitHub Alternatives
While GitHub dominates code hosting, GitHub alternatives exist, each with unique strengths:
- GitLab: Self-hosted or cloud version control with built-in CI/CD, issue tracking, and project management. Ideal for teams wanting an all-in-one DevOps solution.
- Bitbucket (Atlassian): Integrates seamlessly with Jira and Trello. Offers pipelines for CI/CD, self-hosted options.
- Azure DevOps: Microsoft’s suite includes repos, boards, pipelines, test plans, and artifacts. Deep integration with the Azure cloud.
- SourceForge: Older platform focused on open-source projects; less popular today.
- Codeberg/GitBucket/Gitea: Open-source GitHub alternatives for self-hosting. Suitable for privacy-conscious teams.
When evaluating alternatives, consider factors like cost, integration with existing tools, and whether you need advanced DevOps capabilities or a simple repository.
Tips & Best Practices for Using GitHub
- 🌿 Branching strategy: Use GitFlow or a similar model. Work in feature branches, avoid direct commits to
main. - 📝 Commit messages: Write clear, present-tense summaries. Reference issue numbers when relevant.
- 🔀 Pull requests: Create PRs for all code changes; encourage thorough reviews.
- ✅ Code reviews: Require approvals before merging. Add status checks and auto-merge for speed.
- 🤖 Automation with Actions: Run tests, linting, deployments, and assign reviewers automatically.
- 📚 Documentation: Use README file, wiki pages, and CONTRIBUTING guides updated.
- 🏷️ Issues & labels: Track bugs, tasks, and enhancements. Use labels for filtering.
- 🔐 Sensitive data: Add secrets to
.gitignore, store keys in environment variables. - 🛡️ Security: Enable 2FA and review permissions for third-party apps.
- 💾 Backup & mirror: Regularly mirror repos or download copies of critical code.
FAQ
What is GitHub used for?
GitHub is used for hosting code (learn how to host a site or project), tracking changes (version control), collaborating on projects via issues and pull requests, and managing software development workflows. It supports open-source and private projects.
What is a pull request in GitHub?
A pull request is a request to merge changes from one branch into another (often from a feature branch into the main branch). It facilitates code review and automated checks before merging.
Does GitHub track time?
No. GitHub doesn’t track time spent on issues. Use integrations like Everhour, Harvest or Toggl to track time within issues and pull requests.
Is GitHub Copilot free?
GitHub Copilot typically requires a subscription (monthly/yearly). Students and maintainers of popular open-source projects may get discounts or free access.
Can non-developers use GitHub?
Yes. Designers, project managers, writers and other professionals use GitHub. It’s useful for versioning documents, collaborating on markdown files and tracking tasks.
What are GitHub alternatives?
GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, Gitea and Codeberg are alternative Git hosting platforms. They may offer different features like built-in CI/CD (GitLab) or deeper integration with other tools.
Is GitHub safe?
GitHub implements robust security, but safety also depends on users’ practices: avoid committing secrets, use SSH or personal access tokens, and enable two-factor authentication.
How does Everhour integrate with GitHub?
Everhour adds a time tracking button to issues and pull requests. Users log hours directly in GitHub. Data flows into Everhour’s reports and budgets.
Can I self-host GitHub?
No. GitHub is a cloud service. For self-hosting, use GitLab Community Edition, Gitea or similar.
How does GitHub compare to GitLab?
GitLab offers a more integrated DevOps platform (CI/CD, Docker registry) and self-hosting. GitHub focuses on collaboration and has added GitHub Actions for CI/CD. Choose based on your infrastructure and workflow needs.
Final Thoughts
GitHub is still the go-to platform for developers. It offers version control, issue tracking, and pull requests—helping teams work together, maintain code quality, and stay transparent. New features like GitHub Copilot (AI coding assistant) and Projects Beta (project management) keep it evolving.
That said, GitHub doesn’t cover everything. It lacks built-in time tracking or budgeting. Tools like Everhour bridge this gap, letting teams track hours on issues, set budgets, and generate reports for better scope and billing control.
🔎 Check out what real users have to say about Everhour:
“I like the great visualization tools including Gantt charts which make it easy to represent information and invoicing.” [Njeru, Capterra]
“The setup is easy. The interface is really intuitive. I love that it integrates with other systems seamlessly and any calls to support have been answered promptly.” [Chris, Capterra]
“The reporting feature is so easy to use and can be configured any way we need. It’s much stronger than other tools we’ve used in the past. It also integrates so well with our project management software.” [G2]
When picking a platform, think about your team’s size, workflow, and toolchain. GitHub shines with its ecosystem and community. But GitLab or Bitbucket may be better if you need stronger CI/CD or Jira integration. If budgets and hours matter, add Everhour or a similar tool to your stack.
In the end, success depends on the right mix of tools and practices—clear branching, solid code reviews, automation, and open collaboration. With the right setup, GitHub can support projects of any size.
Also, learn how to improve developer productivity with the help of the best developer productivity tools in our guide!

