In any project or business operation, clear and consistent communication is vital for success. One key tool in this communication toolkit is the status report. Understanding how to create and utilize project status reports effectively is crucial for ensuring transparency and maintaining momentum. This article will explore the fundamentals of status reports, including their purpose, types, project status templates, and best practices. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to leverage status reports in project management and drive success in your projects and business activities.
What is a Project Status Report?
A project status report is a document that provides a snapshot of the current state of a project at a specific point in time. It is used to communicate progress, challenges, and key updates to stakeholders, team members, and management. The primary goal of project status reporting is to ensure everyone involved in the project is informed and aligned, helping to keep the project on track and achieve its objectives.
Purpose of a project status report
- Communication: Keeps all stakeholders informed about the project’s progress and any issues that may arise.
- Transparency: Provides a clear view of what has been achieved and what challenges are being faced.
- Decision-making: Helps project managers and stakeholders make informed decisions based on the current status and any emerging risks or issues.
- Tracking progress: Allows for the monitoring of progress against the project plan and helps ensure that the project stays on track.
Regularly updating and distributing project status reports is crucial for keeping teams aligned, addressing issues promptly, and driving projects toward successful completion. To enhance this process, consider using the best time tracking software.
Types of Status Reports
Status reports come in various formats and serve different purposes, depending on the needs of the project and its stakeholders. Here are the common types of status reports:
1. Daily status report
- Purpose: Provides a brief update on the project’s daily progress, including completed tasks, ongoing work, and any immediate issues.
- Format: Typically short and focused on daily activities, often used in projects with fast-paced or high-volume work.
- Content: Summary of tasks completed, work in progress, and any urgent issues or decisions needed.
2. Weekly status report
- Purpose: The project management weekly status report offers a more detailed update on the project’s weekly progress, including achievements, challenges, and upcoming tasks.
- Format: Includes more comprehensive information than a daily report, often with charts or graphs to illustrate progress.
- Content: Overview of the week’s accomplishments, status of key milestones, any issues or risks, and plans for the upcoming week.
3. Monthly status report
- Purpose: Provides an in-depth review of the project’s progress over the month, focusing on long-term trends and overall performance.
- Format: Detailed report with extensive data, analysis, and projections. Often includes executive summaries and detailed appendices.
- Content: Detailed progress against milestones, budget analysis, resource usage, significant challenges, and a summary of next month’s objectives.
4. Quarterly status report
- Purpose: Reviews the project’s performance over a three-month period, highlighting major achievements and long-term trends.
- Format: Comprehensive report with detailed analysis, often used for high-level stakeholders and senior management.
- Content: Summary of quarterly achievements, financial performance, risk management, strategic alignment, and an overview of plans for the next quarter.
5. Status report for stakeholders
- Purpose: Tailored for external stakeholders, including clients, investors, or senior executives, focusing on high-level information and strategic insights.
- Format: Focused on strategic outcomes, often with an emphasis on how the project aligns with broader organizational goals.
- Content: High-level summary of project progress, key achievements, strategic impact, and major risks or issues.
6. Project health report
- Purpose: Provides an overall assessment of the project’s health, including performance, scope, schedule, and budget.
- Format: Detailed report with a focus on project metrics, health indicators, and an assessment of overall project viability.
- Content: Evaluation of project performance, status of key metrics, risk assessment, and recommendations for corrective actions.
Pros of Status Reports
Status reports play a crucial role in project management by providing structured updates and insights into project progress. Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Enhanced communication
- Clarity and consistency: Status reports ensure that all stakeholders receive consistent and clear information about the project’s progress. This helps in avoiding misunderstandings and miscommunications.
- Regular updates: They provide regular updates, keeping everyone informed about current activities, changes, and developments.
![what is shift planning? [benefits & best solution in 2023]](https://blog-cdn.everhour.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/communication-1.gif)
2. Improved project tracking
- Progress monitoring: Status reports help in project tracking against planned objectives and milestones. This allows project managers to identify whether the project is on schedule and within scope.
- Early detection of issues: By regularly reviewing status reports, project managers can quickly identify and address issues or deviations from the plan before they escalate.
3. Informed decision-making
- Data-driven decisions: Status reports provide essential data and insights, allowing stakeholders and project managers to make informed decisions based on current project status and performance.
- Risk management: They highlight potential risks and issues, enabling proactive risk management and mitigation strategies.
4. Accountability and transparency
- Clear accountability: Status reports outline who is responsible for specific tasks and deliverables, promoting accountability among team members and departments.
- Transparency: They offer a transparent view of project progress and challenges, fostering trust among stakeholders and ensuring that everyone is aware of the project’s status.
5. Documentation and record keeping
- Historical record: Status reports serve as a historical record of the project’s progress, decisions, and changes. This documentation can be valuable for future reference, audits, and project reviews.
- Performance evaluation: They provide a basis for evaluating project performance and learning from past experiences to improve future projects.
6. Alignment with goals
- Strategic alignment: Regular status reports help ensure that the project remains aligned with organizational goals and strategic objectives. They provide insights into how project outcomes contribute to broader business objectives.
- Goal tracking: They track progress towards specific project goals and milestones, helping to maintain focus and direction.
7. Motivation and morale
- Team recognition: Status reports can highlight team achievements and progress, boosting morale and motivation by acknowledging the efforts of team members.
- Progress visibility: Seeing documented progress and successes can keep the team motivated and engaged in their work.

8. Effective stakeholder management
- Stakeholder engagement: Regularly updated status reports keep stakeholders engaged and informed, which helps in managing their expectations and addressing any concerns they may have.
- Feedback mechanism: They provide a platform for stakeholders to offer feedback, which can be used to make adjustments and improvements to the project.
How to Write a Status Report
Writing an effective status report is crucial for maintaining transparency, tracking progress, and ensuring that all stakeholders are informed. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to write a project progress template that communicates key information clearly and effectively:
1. Understand the purpose and audience
- Determine objectives: Before writing, clarify the purpose of the report. Are you providing a regular update, addressing specific issues, or summarizing progress for a particular period?
- Identify the audience: Tailor the content to your audience, whether it’s project stakeholders, team members, or senior management. Consider their needs, expectations, and the level of detail required.
2. Choose the right format
- Standardized templates: Use a standardized template if available to ensure consistency and completeness. Templates often include sections for key information and are designed to meet organizational standards.
- Customization: Customize the format as needed to fit the specific requirements of the project or organization. Ensure it aligns with any reporting guidelines or protocols in place.
![status report 101: create clear and actionable reports [2024]](https://blog-cdn.everhour.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Status-Report-Screenshot-1.jpg)
3. Include key sections
- Title and date: Clearly state the title of the report, including the project name and reporting period. Include the date of the report for reference.
- Executive summary: Provide a brief overview of the key points from the report. Summarize progress, major accomplishments, and any critical issues or risks. This section should be concise and informative.
- Project status: Include a snapshot of the project’s overall status (e.g., on track, at risk, delayed). Use status indicators or traffic lights (e.g., green, yellow, red) for visual clarity.
- Milestones and deliverables: List completed, ongoing, and upcoming milestones and deliverables. Include completion dates and any deviations from the plan.
- Progress update: Detail the progress made during the reporting period. Include updates on tasks, achievements, and any changes to the project scope or timeline.
- Budget and resources: Provide an update on the project budget and resource utilization. Highlight any variances from the planned budget and explain significant changes or issues.
- Issues and risks: Identify current issues and risks affecting the project. Describe their impact, the actions being taken to address them, and any potential implications.
- Next steps and actions: Outline the next steps and actions to be taken. Include responsibilities and deadlines for upcoming tasks and milestones.
- Attachments and supporting documents: Attach any relevant documents or data that support the information in the report, such as charts, graphs, or detailed financial reports.
4. Write clearly and concisely
- Use simple language: Avoid jargon or technical language that may not be understood by all readers. Use clear and straightforward language to convey information effectively.
- Be concise: Present information in a concise manner. Focus on key points and avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main message.
- Be accurate: Ensure that all information is accurate and up-to-date. Verify facts and figures to maintain credibility and reliability.
5. Use visual aids
- Charts and graphs: Incorporate charts, graphs, and tables to visualize data and trends. Visual aids can help readers quickly grasp complex information and identify patterns.
- Status indicators: Use visual indicators, such as color-coded status symbols, to highlight the project’s status, progress, and issues. This makes it easier for readers to understand the overall picture at a glance.
![status report 101: create clear and actionable reports [2024]](https://blog-cdn.everhour.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/status-report-chart.jpg)
6. Review and edit
- Proofread: Carefully review the report for spelling, grammar, and formatting errors. Ensure that the content is coherent and well-organized.
- Seek feedback: If possible, have a colleague or team member review the report before finalizing it. Their feedback can help identify any gaps or areas for improvement.
7. Distribute the report
- Share with stakeholders: Distribute the report to all relevant stakeholders and team members. Ensure that it reaches the intended audience in a timely manner.
- Follow up: Be prepared to address any questions or feedback from the recipients. Follow up as needed to provide additional information or clarification.
Status Report Example
To illustrate how to create an effective status report, here’s a project status report template based on a fictional project. This example covers all the key sections and provides a clear, concise overview of project status.
Project Status Report
Title: Website Redesign Project Status Report
Date: August 21, 2024
Executive Summary
The Website Redesign Project is progressing as planned, with significant milestones achieved this period. The design phase is complete, and development is underway. We are on track to meet our project deadlines, although there are minor budget variances that need attention. No major issues or risks have been identified.
Project Status
- Overall Status: On Track
- Status Indicator: 🟢 (Green)
Milestones and Deliverables
| Milestone/Deliverable | Status | Completion Date | Comments |
| Finalize Design Phase | Completed | August 15, 2024 | Design phase completed on time. |
| Begin Development | In Progress | August 20, 2024 | Development started on schedule. |
| Initial Testing | Upcoming | September 10, 2024 | Scheduled to start as planned. |
Progress Update
- Design Phase: Completed with all design elements approved by stakeholders. All design files have been handed over to the development team.
- Development Phase: Development of core functionalities is 30% complete. The team is currently working on the user interface and backend integration.
- Content Creation: Content for key pages is being drafted and will be reviewed in the next reporting period.
Resources & Budget
- Budget Status: Minor Variance
- Budget Utilized: $45,000 (out of $50,000 budget)
- Comments: The project is slightly over budget due to additional design revisions. Adjustments are being made to stay within the overall budget.
Issues and Risks
-
Issue: Additional design revisions led to increased costs.
- Impact: Slightly higher budget expenditure.
- Action: Reassess design requirements to avoid further revisions. Seek approval for budget adjustments if necessary.
-
Risk: Potential delay in content creation due to external review processes.
- Impact: Possible impact on the overall project timeline.
- Mitigation: Schedule regular check-ins with the content team and streamline the review process.
Next Steps and Actions
- Complete Development Phase: Continue development work and ensure timely completion of core functionalities. Target completion date: September 15, 2024.
- Prepare for Initial Testing: Begin preparations for initial testing of developed features. Testing phase to start on September 10, 2024.
- Review Budget: Conduct a detailed review of the budget and adjust as needed. Prepare a revised budget report by August 30, 2024.
Attachments and Supporting Documents
- Design Phase Completion Report
- Development Progress Chart
- Revised Budget Breakdown
This sample status report demonstrates how to structure and present essential project information. Your own doesn’t have to look the same way but can be something to start from.
Use Everhour to Streamline Your Status Report
To enhance the efficiency of creating and managing status reports, consider using Everhour, a robust time-tracking and project status reporting tool. Everhour integrates seamlessly with popular project management software and offers features that can streamline your reporting process:
- Automatic time tracking: Everhour automatically tracks the time spent on different tasks and projects. This feature eliminates the need for manual time logging and ensures that your status reports reflect accurate data on project progress.
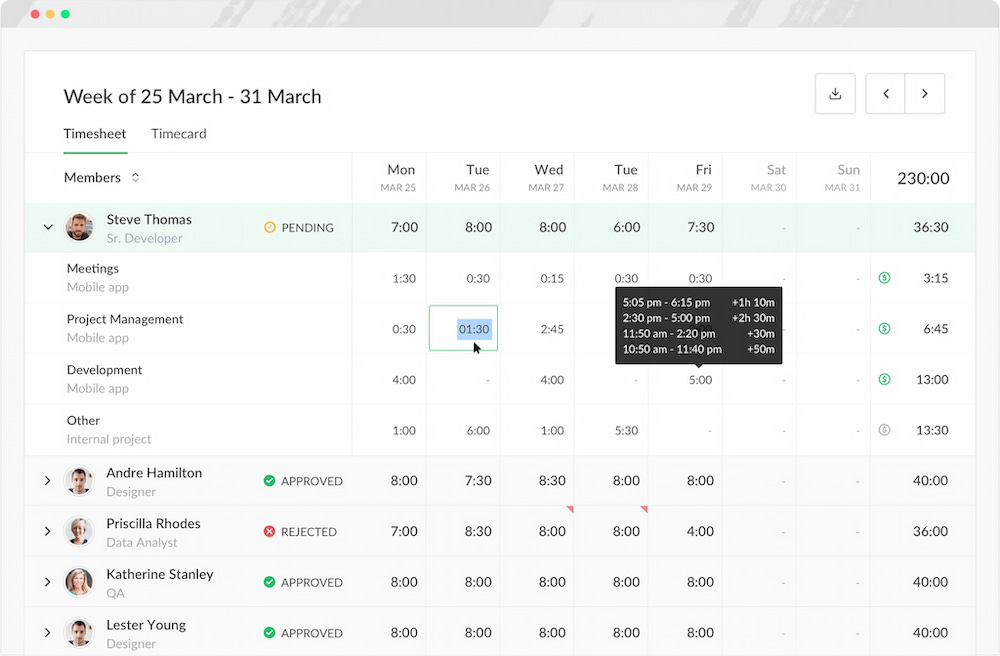
- Real-time insights: With Everhour, you can access real-time data on project milestones, budget utilization, and resource allocation. This immediate visibility allows you to provide up-to-date information in your status reports and make informed decisions quickly.
- Budget tracking: Everhour offers tools to monitor project budgets and expenditures. You can set budget limits and receive alerts if your spending approaches or exceeds the allocated amount. This helps you keep your budget in check and include precise financial details in your reports.
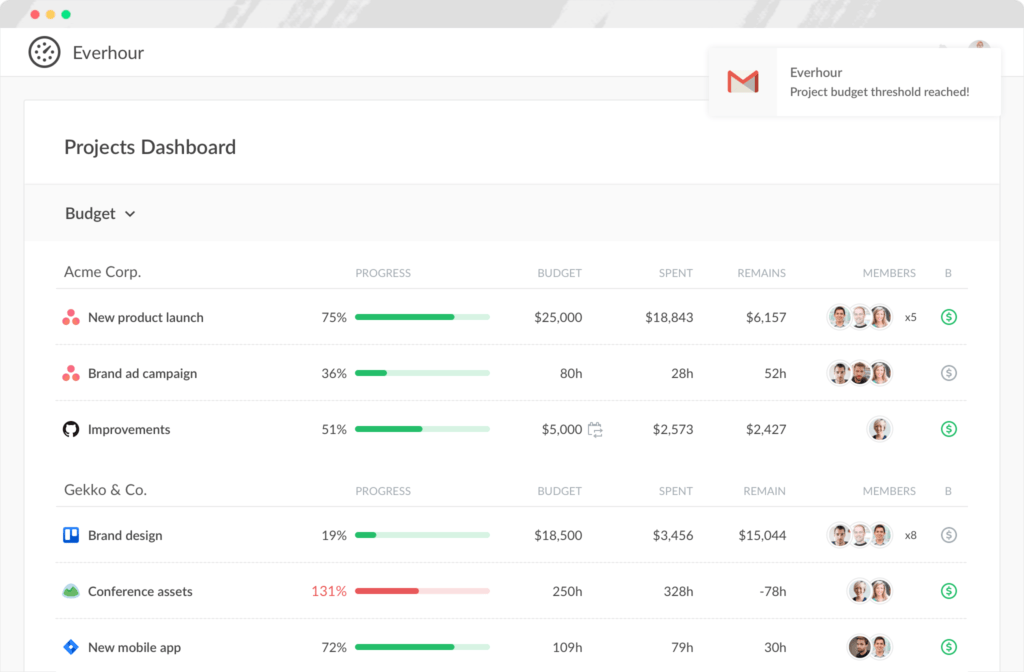
- Customizable reports: Generate detailed status reports with customizable templates in Everhour. Tailor your reports to highlight specific milestones, progress updates, and issues, ensuring that all critical information is communicated clearly and efficiently.
- Seamless integration: Everhour integrates with various project management and collaboration tools, such as Asana, Trello, Notion, ClickUp, and many more. This integration allows for a smooth flow of data between your project management system and status reports, reducing manual entry and minimizing errors.
Learn more about Everhour from this introductory video.
FAQ
1. What should be included in a project status report?
A comprehensive project status report should include:
- Project overview: Brief summary of the project and its objectives.
- Current status: Detailed updates on what has been completed, what is in progress, and what is pending.
- Key milestones: Achieved milestones and upcoming deadlines.
- Issues and risks: Challenges encountered and potential risks, along with mitigation strategies.
- Budget and resources: Current expenditure versus the budget and resource utilization.
- Next steps: Planned actions and changes to address issues or push the project forward.
2. How often should status reports be generated?
The frequency of status reports depends on the project’s complexity and stakeholder requirements. Common intervals are weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly. For high-priority projects or those with tight deadlines, more frequent reports may be necessary.
3. Who should receive the status report?
Status reports should be distributed to key stakeholders, including project sponsors, team members, and clients. The exact recipients may vary based on the project’s nature and the organization’s structure.
4. How can I ensure my status report is effective?
- Be clear and concise: Use straightforward language and avoid jargon.
- Focus on key points: Highlight critical updates, issues, and changes.
- Use visuals: Incorporate charts, graphs, and tables to make data easier to understand.
- Be honest: Report both successes and challenges transparently.
- Follow a template: Consistency helps maintain clarity and make reports easier to follow.
5. How do I handle negative updates in a status report?
When reporting negative updates:
- Be transparent: Clearly describe the issue without sugar-coating.
- Provide context: Explain the impact and why it occurred.
- Propose solutions: Suggest actionable steps to address the issue.
- Stay professional: Maintain a constructive tone and focus on solutions rather than dwelling on problems.
Conclusion
Project reports and status reporting in project management in general are essential for maintaining transparency and managing project progress. By adhering to best practices and utilizing effective tools, you can ensure your reports are clear and actionable.
For a streamlined approach, consider using Everhour. This status report software simplifies time tracking and reporting, helping you create accurate and timely status reports effortlessly.
If you are managing a team of 5 or more and looking to boost efficiency, Everhour is the perfect tool to keep your team on track. With seamless time tracking, you can easily estimate task durations, set clear budgets, and generate detailed reports inside Asana, Trello, Jira, or any other pm tool.
![status report 101: create clear and actionable reports [2024]](https://blog-cdn.everhour.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/jakub-zerdzicki-8wLZi9OhsWU-unsplash.jpg)
