Calculating overtime pay seems pretty simple in theory but if you take different variables into account it can get a tad challenging. Don’t worry: with the help of this concise guide and the best time tracking software, you’ll become a master of it in no time.
Understanding Overtime Pay: What It Means and How to Calculate It
Overtime means that employees should be paid at a higher rate for all hours worked in excess of normal working hours. Normal hours can be determined in different ways: by agreement between employers and workers, by profession, or by legislation. But how much is overtime and how to calculate overtime pay?
In most cases, laws stipulate the standard working hours per week, for example, employees are entitled to overtime pay for every hour beyond 40 they work per week, regardless of how many hours they work in a day.
But in some cases, a standard number of daily working hours are stipulated as well. For example, employees are entitled to overtime for every hour beyond 8 work per day in Alaska, Nevada, Puerto Rico, and the Virgin Islands.
Overtime pay is typically 1.5 times the employee’s regular wage. But in some cases, overtime may be paid at a higher rate. For example, if workers are required to work on a Sunday, they may be paid 2 times their regular rate (i.e., “double time”).
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Overtime Pay
Calculating overtime pay for hourly employees is usually pretty straightforward. Let’s make it clear with an example:
- Mon: 7h total (7 hours regular pay)
- Tue: 9h total (8 hours regular pay + 1h overtime pay)
- Wed: 9h total (8 hours regular pay + 1h overtime pay)
- Thu: 13h total (8 hours regular pay + 4h overtime pay + 1h double overtime)
- Fri: 11h total (7 hours regular pay + 4h paid time off)
- Sat: 9h total (2 hours regular pay + 7h overtime pay)
- Sun: 9h total (9h overtime pay)
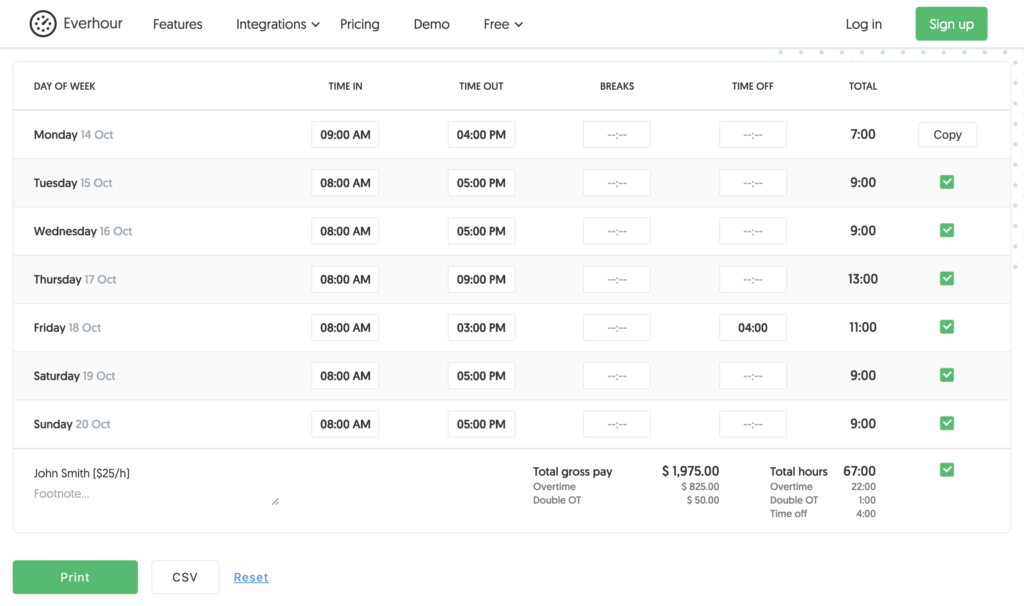
It’s not rocket science, but to help you automate the accurate collection of hours and do proper overtime pay, consider using an online time management tool or a time tracker (Everhour or Gusto). The other solution may be paper time cards and timesheets, Excel files, or Google Spreadsheet forms.
Who Qualifies for Overtime Pay? Rules and Eligibility
Employees can be classified in different ways based on their salary and the type of work they do. Some employees may be exempt from overtime pay if they are employed as executive, administrative, or outside sales workers, as well as certain computer employees. The term “exempt” means exempt from being paid overtime. The full list can be found on the site of the United States Department of Labor.
According to the latest overtime update, since January 1, 2020, any non-exempt employee from the USA who earns less than $684 per week ($35,568 per year) will be also paid overtime.
Remember that misclassifying your employees can result in decreased morale and have significant financial implications. Check out the current rules for your location.
How to Calculate Overtime for Part-Time Employees
The question arises with part-time employees. In general, a full-time employee works, on average, at least 30 hours per week, or 130 hours per month for more than 120 days in a row. A part-time employee works less than 30 hours per week or less than 130 hours per month for more than 120 days in a row.
Part-time employees are not entitled to overtime based on a weekly standard. If you have an exceptionally busy week, however, and you put in 50 hours, you are entitled to overtime pay. And, if you work in a state with a daily overtime standard, you are entitled to overtime if you hit the state threshold.
How to Calculate Overtime Pay: Breakdown by Country
As already mentioned before, a lot depends on the country (and even the state in the USA) and local legislation.
In Canada 🇨🇦, employers may be required to pay overtime at a higher rate, but also be allowed to require time off in lieu (also called “banked time”) at the normal rate. Unless a contract of employment or a collective agreement states otherwise, an employee does not earn overtime pay on a daily basis by working more than a set number of hours a day. Overtime is calculated only on a weekly basis or over a long period under an averaging agreement.
Many employees have jobs that are exempt from the overtime provisions of the Employment Standards Act (e.g. managers and supervisors do not qualify for overtime if the work they do is managerial or supervisory).
In France 🇫🇷, the legal length of the working week is 35 hours in all types of companies. The working day may not exceed 10 hours. Furthermore, employees may not work for more than 4.5 hours without a break. The maximum working day may be extended to 12 hours under a collective agreement.
Breaks, lasting a minimum of 20 minutes, must be granted to the employees at least every 6 hours. All workers have a daily rest period of 11 consecutive hours (9 hours in certain cases depending on collective agreements). The minimum weekly rest period is 35 consecutive hours (11 hours plus a 24 consecutive hour rest period per week).
In Japan 🇯🇵, it is an eight-hour workday and 40-hour workweek with at least one day off per week. It is also required to pay a premium of at least 25% over the ordinary hourly wage for any overtime work, 35% for any work on prescribed off days, and an additional 25% for any work between 10 pm and 5 am.
In California 🇺🇸, any time worked in excess of 8 per day and for the first 8 hours worked on the seventh consecutive day of work is counted as overtime.
Any time worked in excess of 12 hours a day and in excess of 8 hours on the seventh consecutive day of work in the workweek is counted as double time.
Overtime and Time-Off in Lieu
Some employers give you time off instead of paying for overtime. This is known as ‘time off in lieu.” “In lieu” essentially means “instead”. There must be a written agreement between the employer and employee which approves this type of compensation. The employee must also specifically request time off in lieu of overtime pay. The employer cannot impose it unilaterally.
TOIL needs careful management and the ground rules should be set out clearly. With an obvious expiry date — most likely either calendar year-end or financial year-end. You typically also agree on the maximum number of days that one employee can accrue in TOIL.
How to Calculate Overtime Pay: Final Note
If you believe you are not paid properly, bring the issue to the attention of your supervisor or human resources department. If that doesn’t work, you should contact an attorney to explore your legal options.
The information contained in this article is not legal advice and is not a substitute for such advice. Laws change frequently, and the information may not reflect your local laws or the most recent changes to the law.
We provide various articles on the topic, for example, you can learn if mandatory overtime is legal in this article.
If you are managing a team of 5 or more and looking to boost efficiency, Everhour is the perfect tool to keep your team on track. With seamless time tracking, you can easily estimate task durations, set clear budgets, and generate detailed reports inside Asana, Trello, Jira, or any other pm tool.

