When managing expenses for travel or business-related activities, per diem allowances can play a crucial role in budgeting and financial planning. However, one common question arises: is per diem taxable? Understanding the tax implications of per diem can help both employers and employees navigate financial reporting and ensure compliance with IRS regulations. In this article, we’ll break down what per diem is, how it is treated for tax purposes, and what you need to know to manage it effectively. Whether you’re an employer providing per diem or an employee receiving it, this guide will clarify how per diem affects your taxes and offer insights into best practices for reporting and compliance.
What Is a Per Diem Payment?
A per diem pay is a daily allowance provided by employers to employees to cover expenses incurred during work-related travel. This payment typically covers costs such as meals, lodging, and incidental expenses while an employee is away from their usual place of work. Instead of reimbursing employees for actual expenses, which would require submitting receipts and detailed expense reports, employers provide a set per diem rate to simplify the process. Per diem expenses are designed to ease the financial burden on employees during business trips and to streamline the expense management process for employers.
The rates for per diem are often determined by federal guidelines or company policy, and they can vary based on the location and duration of the trip. These rates may differ for meals and incidental expenses (M&IE) compared to lodging costs.
Tax Deductibility of Per Diem
Understanding the tax implications of per diem payments is crucial for both employers and employees to ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid potential penalties. The tax treatment of per diem allowances depends on how they are structured and documented.
For employers
💲 Deducting per diem expenses
- Business expense deduction: Employers can generally deduct per diem payments as legitimate business expenses on their tax returns. These deductions cover costs related to employees’ lodging, meals, and incidental expenses incurred during business travel.
- Adherence to IRS rates: To fully deduct per diem expenses without additional documentation, employers should adhere to the standard per diem rates set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). These rates vary based on the location and time of year and are updated annually.
-
Accountable plan requirements: Per diem payments must be made under an accountable plan to be deductible and non-taxable. An accountable plan requires:
- Business connection: Expenses must have a direct business purpose.
- Substantiation: Employees must provide documentation detailing the amount, time, place, and business purpose of the expenses.
- Return of excess amounts: Any per diem amounts paid in excess of the IRS-approved rates must be returned to the employer within a reasonable time frame.
✅ Benefits of using an accountable plan
- Simplified record-keeping: When following IRS per diem rates under an accountable plan, employers are not required to collect receipts for every expense, simplifying administrative processes.
- Avoidance of payroll taxes: Per diem payments under an accountable plan are not subject to payroll taxes, reducing the overall tax burden for the employer.
- Compliance and risk management: Adhering to IRS guidelines minimizes the risk of audits and associated penalties for misclassification of taxable income.

➕ Excess per diem payments
- Taxable income: If employers provide per diem payments exceeding IRS standard rates and the excess is not returned, the additional amount is considered taxable income to the employee and must be reported on their W-2 form.
- Record-keeping requirements: Employers must keep detailed records and include excess payments in wages, subjecting them to income tax withholding and employment taxes.
For employees
💸 Receiving per diem payments
- Non-taxable allowance: Per diem payments received under an employer’s accountable plan and within IRS-approved rates are not considered part of an employee’s taxable income. Employees are not required to report these amounts on their tax returns.
-
Substantiation obligations: Employees must provide adequate documentation to their employer, including:
- Dates of travel: Clearly stating when the business trip started and ended.
- Location: Specifying the city or area where the business activities occurred.
- Business purpose: Describing the reason for the travel and how it relates to the employer’s business.
❗ Excess per diem and tax implications
- Taxable excess amounts: If employees receive per diem payments exceeding IRS standard rates and do not return the excess, the additional funds are treated as taxable income. This amount should be included in their gross income and reported accordingly.
- Reporting requirements: Excess per diem payments will be reflected on the employee’s W-2 form and are subject to federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes.
- Deductions for unreimbursed expenses: Due to changes in tax laws under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, employees cannot deduct unreimbursed job expenses, including travel costs, on their federal tax returns for tax years 2018 through 2025. This makes proper per diem arrangements even more critical.
🏠 Self-employed individuals
- Per diem deductions: Self-employed individuals can use per diem rates to deduct lodging, meals, and incidental expenses on their tax returns. They must maintain proper records to substantiate their travel expenses, including dates, locations, and business purposes.
- Limitations and compliance: The same IRS rates and rules apply, and self-employed individuals must ensure compliance to avoid issues during tax filings and potential audits.
Important considerations
🗺️ Locality-specific rates
- Understanding variations: Per diem rates vary depending on the travel destination. High-cost areas have higher rates to reflect increased expenses.
- Accessing current rates: Employers and employees should reference the latest IRS per diem rates, available on the IRS website, to ensure accurate and compliant payments.
🤏Partial day travel
- Prorated rates: For travel days that are less than 24 hours, per diem payments should be prorated accordingly. Specific guidelines dictate how much can be claimed for departure and return days.
📚 Record retention
- Duration: Employers and employees should retain all relevant travel and per diem records for at least three years, in case of IRS inquiries or audits.
- Documentation: Records should include travel dates, destinations, purposes, and any receipts or logs that support the per diem claims.

🏛️ State and local taxes
- Variations: State and local tax treatments of per diem payments may differ from federal rules. It is essential to consult relevant state and local tax regulations to ensure comprehensive compliance.
💼 Consulting tax professionals
- Expert guidance: Given the complexities and potential changes in tax laws, consulting with tax professionals or accountants is advisable to navigate per diem tax matters effectively.
Reporting Per Diem to the IRS
When handling per diem payments, both employers and employees must follow IRS guidelines to ensure proper reporting and avoid tax complications. The IRS per diem rules are designed to simplify the process of reimbursing employees for travel expenses, but they also come with specific reporting requirements.
For employers
- Accountable vs. non-accountable plans: Employers must distinguish between per diem payments made under an accountable plan and those under a non-accountable plan. Payments made under an accountable plan that meet IRS per diem guidelines are not taxable and do not need to be reported as wages. However, if the per diem payments exceed the IRS per diem rates or do not meet the accountable plan criteria, the excess amount must be reported as taxable income on the employee’s W-2 form.
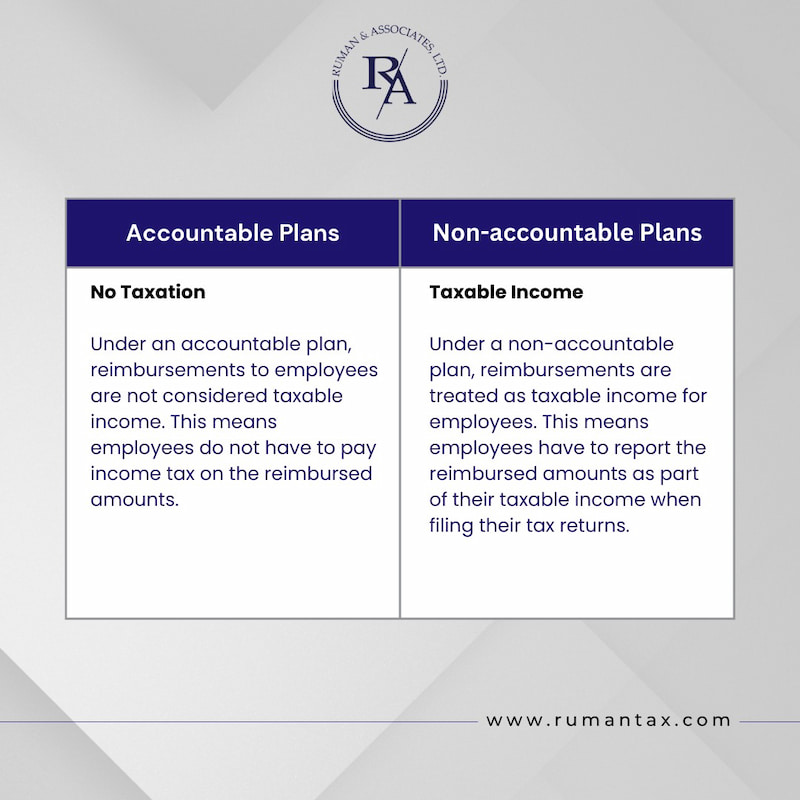
- Record-keeping: Employers should maintain accurate records of all per diem payments, including the amount, purpose, and duration of the employee’s travel. This documentation is essential in case of an IRS audit, ensuring that the per diem payments are compliant with IRS per diem rules.
- IRS per diem rates compliance: To avoid additional tax liabilities, employers should ensure that per diem payments do not exceed the IRS per diem rates for the specific location and time of the travel. The IRS updates these rates annually, and it’s crucial for employers to stay informed of the current rates.
For employees
- Substantiation: Employees should provide necessary documentation to their employers, such as travel dates, destination, and purpose of the trip, to substantiate the per diem payments under an accountable plan. Failure to do so may result in the per diem being treated as taxable income.
- W-2 reporting: If any portion of the per diem is taxable, it will be included in the employee’s W-2 form as wages. Employees should review their W-2 to ensure that all amounts are reported correctly.
- State reporting requirements: In addition to federal reporting, employees should be aware of any state-specific rules regarding per diem. Some states may have different regulations on how per diem is taxed or reported.
Determining Per Diem Rates
Per diem rates are crucial for both employers and employees to ensure compliance with IRS guidelines and to manage travel expenses effectively. These rates are established by the IRS and are used to reimburse employees for daily expenses incurred during business travel, such as lodging, meals, and incidental costs. Understanding how to determine the correct per diem rates is essential for accurate reporting and avoiding tax complications.
How per diem rates are set
- IRS-established rates: The IRS sets per diem rates based on the location of the travel. These rates vary depending on the city or region, reflecting the cost of living in different areas. Higher rates are generally assigned to major cities or areas with a higher cost of living, while lower rates apply to less expensive locations.
- GSA rates: For federal employees and contractors, the General Services Administration (GSA) provides per diem rates, which are commonly used as a benchmark in the private sector. These rates cover lodging, meals, and incidental expenses and are updated annually to reflect changes in travel costs.
- Use of high-low substantiation method: The IRS allows employers to use a simplified method known as the “high-low” substantiation method. This method sets a standard per diem rate for high-cost areas and a lower rate for all other locations, simplifying the process of determining per diem for various travel destinations.
Factors to consider when determining per diem rates
- Travel destination: The specific location of the business travel is the primary factor in determining the applicable per diem rate. Employers should reference the latest IRS per diem rates for the relevant city or region to ensure accurate reimbursement.
- Length of stay: The duration of the employee’s stay can influence the per diem rate, particularly for extended trips. Some employers may choose to adjust the per diem rate for longer stays, while others stick to the standard daily rate.
- Seasonal variations: In some locations, per diem rates may fluctuate based on the time of year, reflecting seasonal changes in travel costs. For example, rates might be higher during peak tourist seasons.
- Company policy: While IRS per diem rates set the maximum allowable limits, companies may establish their own per diem policies within these guidelines. Employers may choose to offer lower rates or provide higher reimbursement rates for specific circumstances, such as international travel.

Importance of accurate per diem rate determination
- Compliance with IRS rules: Using the correct per diem rates ensures that reimbursements are non-taxable and comply with IRS rules. Overpaying or underpaying per diem can lead to tax complications for both the employer and the employee.
- Budget management: Accurately determining per diem rates helps businesses manage travel expenses and avoid unnecessary costs. It also provides employees with clear expectations for their travel budgets.
- Employee satisfaction: Providing fair and appropriate per diem rates ensures that employees are adequately compensated for their travel expenses, contributing to overall job satisfaction and productivity.
Alternatives to Per Diem
While per diem is a popular method for reimbursing employees for travel expenses, there are several alternatives that businesses can consider. These options offer flexibility and may better suit certain scenarios or company policies. Exploring these alternatives can help businesses manage travel costs effectively and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Reimbursement of actual expenses
- Direct expense reimbursement: Instead of providing a per diem, employers can reimburse employees for the actual expenses incurred during business travel. Employees must submit detailed receipts and documentation for lodging, meals, transportation, and other costs. This method ensures that employees are reimbursed for the exact amount spent, but it requires meticulous record-keeping and processing.
- Expense reporting systems: Utilizing expense reporting software can streamline the process of reimbursing actual expenses. These systems allow employees to upload receipts and track expenditures, simplifying the approval and reimbursement process for employers.
Travel and corporate credit cards
- Corporate credit cards: Providing employees with corporate credit cards for business travel can simplify expense tracking and management. This method allows for direct billing to the company and can reduce the need for expense reports and reimbursements. It also provides a clear record of expenses for accounting purposes.
- Travel management services: Partnering with a travel management company can help companies manage travel expenses more effectively. These services often include booking and managing travel arrangements, as well as providing detailed reports on travel spending.
Fixed allowances
- Expense allowances: Instead of per diem, companies may offer fixed allowances for specific travel expenses. For example, employees may receive a set amount for meals or transportation, regardless of the actual amount spent. This approach provides flexibility while controlling costs and reducing administrative burden.
- Lump-sum payments: Companies might offer lump-sum payments to cover travel expenses. This method provides employees with a predetermined amount of money for their trip, allowing them to manage their expenses as they see fit.
Can I write off travel expenses for work?
Employees may be able to deduct unreimbursed travel expenses on their personal tax returns if they meet specific criteria set by the IRS. However, recent changes in tax laws have limited these deductions for employees who are not self-employed. It is essential to consult with a tax advisor to understand eligibility and ensure compliance with current tax regulations.
Choosing the right approach
The choice between per diem and its alternatives should consider both business needs and employee preferences. Some companies may find per diem easier to manage, while others may prefer reimbursing actual expenses or offering allowances.
Evaluating the administrative complexity and compliance requirements of each method is crucial. Per diem can simplify expense management, but alternatives may offer more precise reimbursement aligned with actual costs.
Is Per Diem Taxable: Conclusion
Understanding is per diem taxable is crucial for both employers and employees involved in business travel. Whether choosing to use per diem or exploring alternatives like actual expense reimbursement, fixed allowances, or travel management tools, it’s important to select a method that aligns with your business needs and ensures compliance with IRS regulations.
For streamlined expense tracking and efficient management of travel costs, tools like Everhour can be a valuable asset. Everhour’s time tracking and expense management features integrate seamlessly with popular project management tools, offering a user-friendly solution for tracking and reporting expenses accurately. By using Everhour, businesses can simplify the expense reimbursement process, maintain precise records, and stay organized.
If you are managing a team of 5 or more and looking to boost efficiency, Everhour is the perfect tool to keep your team on track. With seamless time tracking, you can easily estimate task durations, set clear budgets, and generate detailed reports inside Asana, Trello, Jira, or any other pm tool.

