Corporate level strategy is a crucial aspect of organizational management that involves setting the overall direction for a company and determining how to allocate resources across its various business units. It serves as a roadmap for achieving long-term success by focusing on high-level objectives, such as growth, diversification, and competitive positioning. In today’s dynamic business environment, companies must craft strategies that not only address current market challenges but also anticipate future trends. This article delves into the key components of corporate level strategy, explores various strategic options, and discusses how companies can effectively formulate, implement, and monitor their strategies to drive sustainable success.
What is Corporate-Level Strategy?
Corporate level strategy refers to the overarching strategy of a company that focuses on managing its various business units or subsidiaries. It defines the company’s scope, competitive advantage, and resource allocation to achieve long-term objectives. Unlike business level strategies that concentrate on individual markets or products, corporate level strategies address broader goals such as growth, diversification, mergers, acquisitions, or restructuring. The goal is to create value by optimizing the company’s overall portfolio and ensuring synergy between different units.
Key aspects of corporate level strategy include:
- Resource allocation: Deciding how to distribute resources across various divisions to maximize overall performance.
- Diversification: Expanding into new markets or product lines to reduce risk and increase revenue streams.
- Mergers and acquisitions: Pursuing growth through the purchase of or partnership with other companies.
- Strategic alliances: Collaborating with other organizations to leverage complementary strengths.
In essence, corporate level strategy is about positioning the company in the market and determining the best way to achieve sustained success across its entire business portfolio.
Types of Business Strategy
Business strategy encompasses a variety of approaches and methods to ensure an organization’s growth and competitiveness. Broadly, strategies are categorized into three levels: corporate level strategy, business level strategy, and functional level strategy. Each level addresses a different set of concerns and operates at different points within the organizational hierarchy.
1️⃣ Corporate level strategy
Corporate level strategy is concerned with the overall direction and scope of the organization. This strategy focuses on decisions made at the highest levels, typically by the CEO and top management, and it addresses questions like:
🌟 What industries or markets should the company operate in?
🌟 Should the company grow through mergers, acquisitions, or organic expansion?
🌟 Should the organization diversify or specialize?
At this level, the organization considers how to balance its portfolio of businesses and resources. Corporate level strategy focuses on creating value across multiple business units or sectors. The key goal is to align various parts of the organization with long-term growth and profitability objectives.
Types of corporate level strategy
There are several types of corporate level strategies, each suitable for different circumstances:
- Growth strategy: A growth strategy focuses on expanding the company’s operations. This could involve entering new markets, increasing market share, or developing new products. Companies may pursue organic growth, where they build internally, or inorganic growth, which involves mergers or acquisitions.
- Stability strategy: A stability strategy aims to maintain the current business status by keeping operations steady and predictable. It’s typically used when a company is in a mature or saturated market, where growth is minimal. The focus here is on consolidating current gains rather than expanding aggressively.
- Retrenchment strategy: Retrenchment strategies are applied when a company needs to reduce its size or scale down operations. This may involve cost-cutting, divesting non-core business units, or restructuring. The aim is to improve efficiency and focus on the most profitable areas.
- Diversification strategy: Diversification involves entering new industries or markets to spread risk. A company might diversify into related areas (related diversification) or completely new, unrelated industries (unrelated diversification). This strategy helps companies reduce dependence on a single industry.
These strategies help corporate leaders determine the overall direction of the organization and ensure that resources are allocated effectively.
2️⃣ Business level strategy
Business level strategy focuses on how a company competes within a specific industry or market. It is developed by divisional or middle management and looks at how to position the business relative to competitors. Common types of business level strategies include:
- Cost leadership: This strategy focuses on becoming the lowest-cost producer in the industry. Companies that succeed with cost leadership can offer products or services at a lower price than competitors while maintaining profitability.
- Differentiation: In a differentiation strategy, businesses offer unique products or services that stand out from competitors. These businesses often emphasize quality, features, or branding to make their offerings more attractive.
- Focus strategy: A focus strategy involves targeting a specific niche market or customer segment. Companies can pursue this by either focusing on cost leadership or differentiation within that niche.
3️⃣ Functional level strategy
Functional level strategy operates at the departmental level within an organization. It involves decisions and actions taken within specific functions such as marketing, HR, finance, and operations. Functional strategies support higher-level corporate and business strategies by optimizing performance in particular areas.
For instance, a marketing strategy might focus on improving customer engagement through digital campaigns, while a human resources strategy could center on enhancing talent acquisition and employee retention.
Corporate Level Strategy Characteristics
Corporate level strategy has several key characteristics that define its focus and scope. These characteristics help guide top management in making long-term decisions about the direction and resource allocation of the entire organization. Here are the main traits of corporate level strategy:
🎯 Long-term focus
Corporate level strategy is inherently long-term, aiming to steer the organization toward sustained growth and profitability. Decisions at this level consider the company’s future trajectory, often spanning several years or even decades. Leaders must evaluate long-term trends and emerging opportunities, making strategic decisions that ensure the organization remains competitive and profitable over time.
🗂️ Resource allocation
One of the central aspects of corporate level strategy is the allocation of resources. This includes financial, human, and operational resources, which need to be distributed across various business units, departments, and projects. Effective resource management ensures that high-priority areas receive the support they need for growth and innovation, while underperforming segments are adjusted or eliminated. (Make sure to use the best resource management software to cover all your business’s needs in that respect.)
🌐 Diversification
Diversification is a prominent feature of corporate level strategy, particularly for companies looking to reduce risks by entering new markets or industries. A company might pursue related diversification (entering a new market or sector that is related to its existing business) or unrelated diversification (expanding into completely different industries). Diversification strategies help spread risk and can enhance growth potential in unfamiliar or competitive markets.
🧩 Synergy across business units
Corporate level strategy often seeks synergy between different parts of the organization. This means creating efficiencies and opportunities for collaboration between business units. Synergies can take the form of shared knowledge, technology, or distribution channels. The idea is that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts, and strategic decisions should reinforce the capabilities of different units to maximize the company’s overall value.
🕹️ Strategic control and oversight
At the corporate level, senior leadership must exercise strategic control and oversight of various business units. While each division or unit may have its own business level strategy, corporate leaders ensure that these strategies align with the overall goals of the organization. This may involve performance monitoring, setting benchmarks, and making adjustments where necessary to ensure the company stays on course.
🛡️ Risk management
Corporate level strategy involves evaluating and managing risks across the entire organization. This includes assessing the potential risks associated with new markets, acquisitions, or product development. Effective risk management ensures that the company can respond to challenges without jeopardizing its long-term viability. Corporate leaders must weigh potential rewards against risks to make informed strategic decisions.
🔗 Strategic fit and alignment
A key characteristic of corporate level strategy is ensuring strategic fit and alignment between different units or departments. This alignment ensures that business activities complement and support one another. If a company is involved in multiple industries or markets, each division’s goals and activities must align with the company’s overarching strategy, creating a coherent direction for the entire organization.
Corporate Level Strategy Examples
Corporate level strategies are often deployed to guide a company’s direction, expansion, and positioning across industries or markets. Here are some common examples of corporate level strategies that organizations use to achieve long-term growth and competitive advantage:
Market expansion
Market expansion involves growing into new geographical areas or demographic segments. By moving into untapped markets, companies can reach new customers and diversify their customer base. This strategy may require adapting products, marketing approaches, or services to align with local preferences and regulations.

Related diversification
Related diversification is when companies expand into new products or services that are closely linked to their existing offerings. For example, a company known for home appliances might branch into home automation technology. This approach leverages existing resources and expertise to create complementary products that appeal to the same customer base, increasing brand loyalty and product cross-sales.
Unrelated diversification
Unrelated diversification is the expansion into entirely new industries or product categories. This strategy helps companies spread risk by balancing business units across different markets. By diversifying outside of their core industry, companies can stabilize earnings, even if one sector faces a downturn.
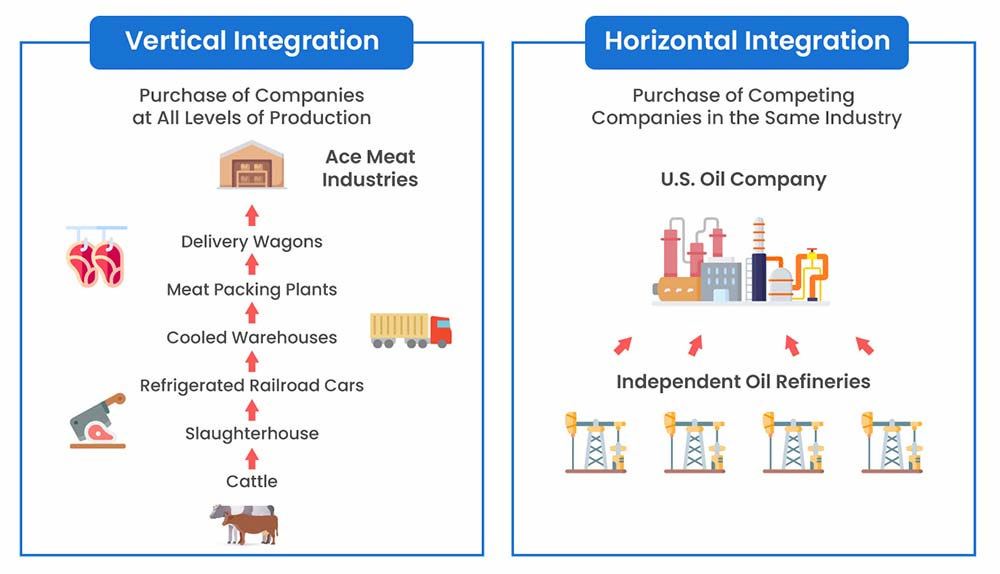
Vertical integration
Vertical integration involves controlling more of the supply chain, either by bringing in-house raw material production or controlling finished product distribution. Through backward integration, companies manage production processes or suppliers, while forward integration involves gaining control over distribution channels or retail. This integration can reduce costs and improve efficiency.
Strategic alliances and partnerships
Strategic alliances and partnerships allow companies to share resources, expertise, or technology without merging or acquiring another company. Through alliances, companies can quickly access new technologies or enter markets with reduced risks and investments.
Mergers and acquisitions
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) enable a company to acquire another business, gain its resources, or eliminate a competitor. Acquisitions can strengthen a company’s market share, provide access to new technology, or expand into new markets. Mergers and acquisitions require a significant capital investment but can yield substantial returns when strategically aligned with company goals.
Globalization
Globalization involves standardizing products or services across multiple international markets, aiming for economies of scale and uniform branding. By creating a unified product that appeals to a broad audience, companies can reduce costs and increase profitability. However, globalization requires a solid understanding of international markets to balance local demands with global efficiency.
Product development
In product development, companies innovate within their current market to create new products that meet evolving customer needs. This strategy allows businesses to retain existing customers by offering them updated or entirely new versions of products they already use. Technology companies often use this approach to maintain relevance, like smartphone manufacturers who regularly release upgraded models.
Outsourcing and offshoring
By outsourcing or offshoring parts of the production process, companies focus on core competencies while reducing costs. Outsourcing typically involves hiring external outsourcing companies to handle certain business functions (e.g., customer support), while offshoring shifts parts of the production process to lower-cost international locations. Both approaches help reduce operating expenses and increase efficiency.
Digital transformation
Digital transformation leverages technology to improve efficiency and enhance customer experiences. Companies using this strategy implement advanced tech solutions, like cloud computing, data analytics, or AI, to streamline operations and create more flexible business models. Digital transformation has become particularly popular in industries like finance, healthcare, and retail, as it supports better decision-making and often provides a competitive edge.
Benefits of Corporate-Level Strategy
A well-designed corporate level strategy offers multiple advantages that can drive a company’s growth and competitiveness. Here are some key benefits:
- 🔄 Enhanced resource allocation: Corporate level strategies, like the ones shown in various corporate strategy examples, allow companies to better distribute resources across different business units. This improves efficiency and helps prioritize high-impact areas, particularly when dealing with multiple product lines or markets.
- 🌐 Risk management and diversification: High level strategies, such as unrelated diversification, help companies manage risk by spreading their investments across different markets. Diversifying into unrelated sectors can stabilize overall revenue, even when one industry faces a downturn.
- 🏆 Competitive advantage: Strategies like market expansion or vertical integration provide firms with unique ways to stand out. For example, companies that vertically integrate can reduce their dependency on external suppliers or distributors, potentially lowering costs and improving product quality.
- 📈 Scalability and growth potential: A well-structured corporate level strategy enables companies to scale operations efficiently, often by leveraging economies of scale. Expanding to international markets opens new revenue streams, allowing firms to grow beyond the constraints of their domestic market.
- 🧠 Improved decision-making: High-level strategies offer a framework for decision-making that aligns with the company’s long-term goals. This clarity enables leaders to make more informed choices about investments, divestments, and other critical moves, ensuring that each decision supports the overall corporate vision.
- 🔗 Better alignment of business units: By using corporate level strategies, businesses ensure alignment across all departments and subsidiaries. For instance, companies engaging in related diversification can create synergies between different product lines, enhancing brand loyalty and cross-sales.
These benefits illustrate how corporate level strategy is essential for building a resilient and adaptable organization, as it encourages companies to proactively position themselves for long-term success in a dynamic market environment.
Conclusion
Corporate level strategies offer companies a roadmap to achieving long-term growth, stability, and competitive advantage. By exploring different options, businesses can effectively manage risk, align resources, and create new revenue opportunities. Choosing the right strategy requires understanding your company’s core competencies, market conditions, and growth objectives.
For companies aiming to improve operational efficiency and manage resources strategically, tools like Everhour can be invaluable. Everhour enables teams to track project hours and costs accurately, ensuring that resource allocation aligns with overarching corporate strategies. With clear insights into time and expense tracking, businesses can better execute their corporate level strategies, monitor performance, and make data-driven decisions that support their high-level goals.
If you are managing a team of 5 or more and looking to boost efficiency, Everhour is a perfect time tracker to keep your team on track. With seamless time tracking, you can easily estimate task durations, set clear budgets, and generate detailed reports inside Asana, Trello, Jira, or any other pm tool.

