“Working 9 to 5, what a way to make a living,” as the famous song by music legend Dolly Parton goes. But have you ever wondered why the 9 to 5 schedule became so popular? Is it the most effective way of working? Or are you and your team working too much? Join us and find out all you need to know about average working hours throughout history.
Today vs. 100 Years Ago: How Many Work Hours in a Year?
Back in hunter-gatherer societies, the average working day was around three to five hours (but up to eight if you include food prep). And that’s just as well, as the average lifespan at the time was between 21 and 37 years.
Since then, a lot has changed. Lifestyles have shifted, and we’ve become a more modern society. And that seems to mean working more. But why? And is it effective? For starters, let’s take a look at how working life has changed throughout history.
❗ To navigate this evolving landscape, using the best time tracking software can help ensure you and your team maintain a balanced workload.
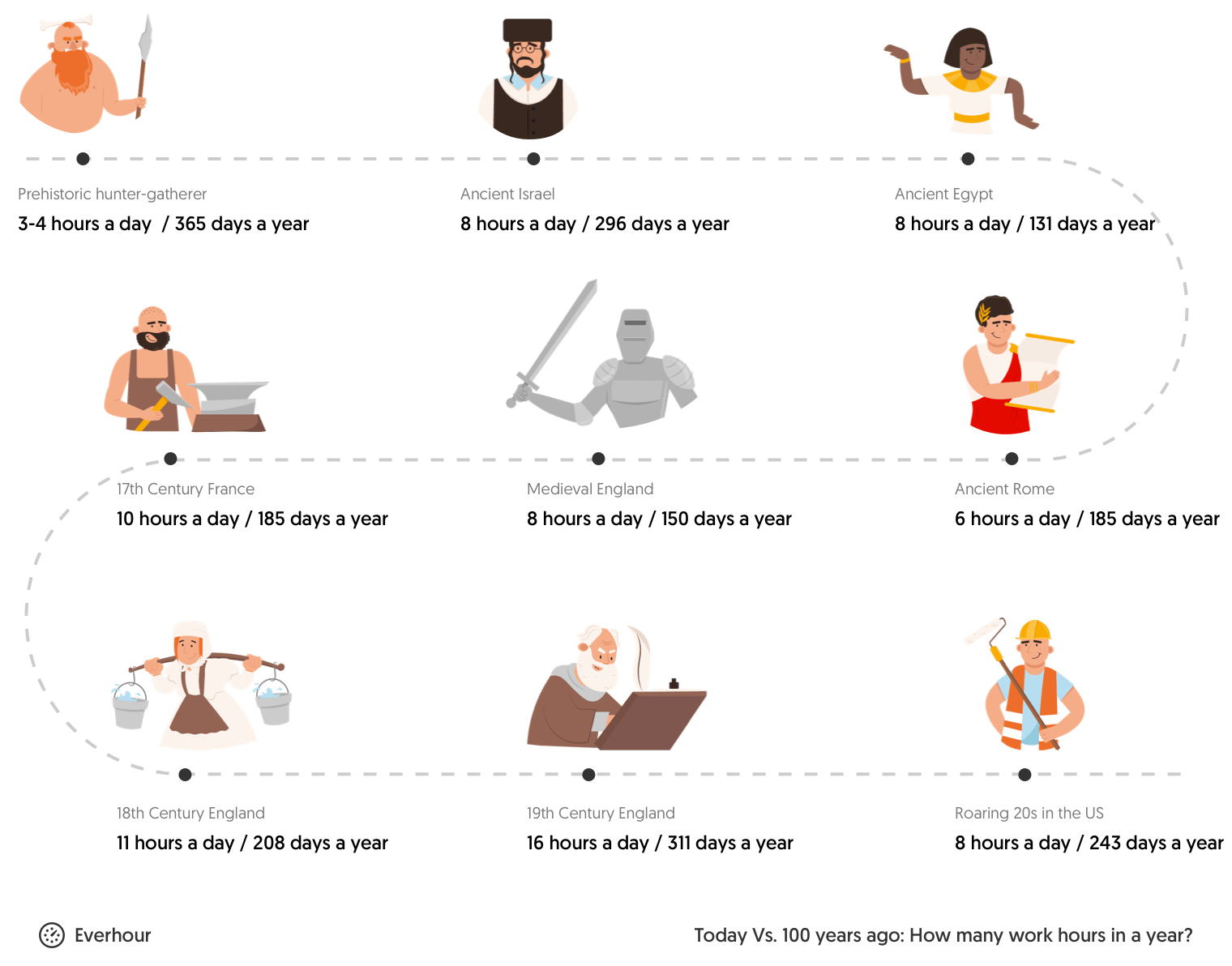
What are the average hours worked per week?
Nowadays, according to US labor law, a full-time workweek equals 40 hours. Multiplied by 52 weeks, that’s 2,080 hours per year. But most people don’t actually work that much.
- Global average: Around 35 hours/week, or 1,820 hours/year
- Monthly average: About 176 hours
- Part-time or statutory employees may work even less
Working hours have changed over time due to historical and economic factors. Let’s take a look at how working hours evolved over the last 70 years:
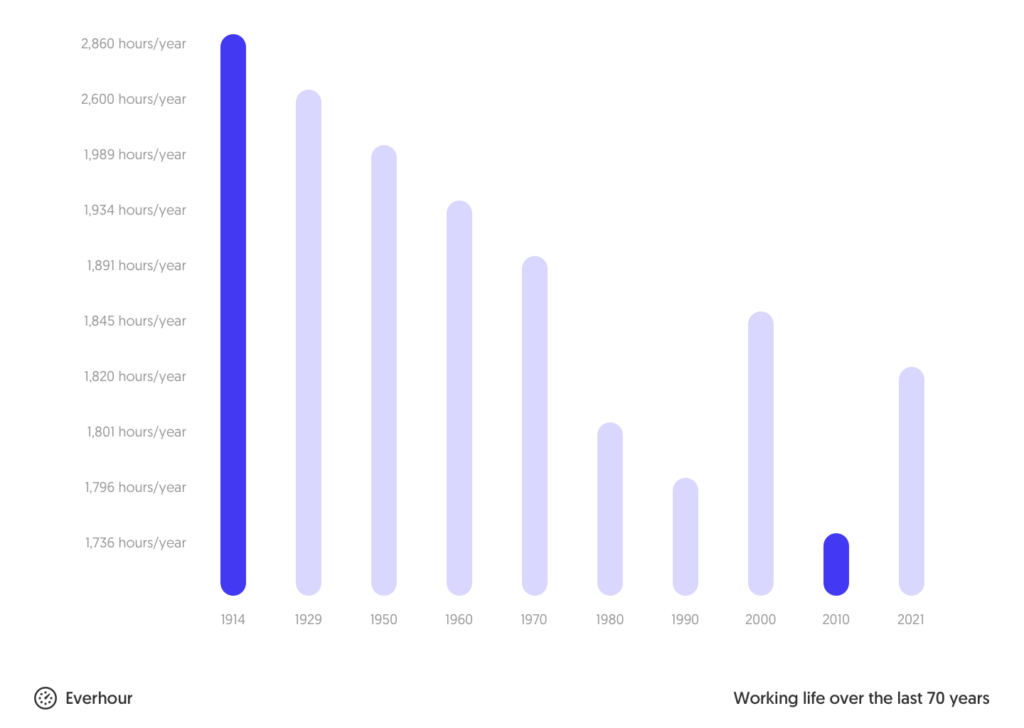
- 1914 (WWI): Average was 55 hours/week, with some workers doing 72 hours to meet wartime demands
- But productivity declined beyond 40 hours/week (source)
- 1926: Henry Ford introduced the 9-to-5, 40-hour week
- 1930s: During the Great Depression, many still worked 46–50 hours/week
- Post-WWII: The 40-hour week became standard
- Today, employers are exploring new models like the 9/80 schedule and 4-day workweeks
What Is the Average Working Year?
It might seem that the work never ends, but how much are we really working? Let’s take a look at the average working year as it stands today.
Number of hours in a year vs. how many you spend working
It might feel like work takes up most of your life. But how does it compare to the total number of hours in a year? Here’s a quick breakdown:

And don’t forget about leap years! Every four years, February gains an extra day—adding 24 hours and bringing the total to 8,784 hours.
If you worked the global average of 1,820 hours in 2023, then about 20.78% of your entire year was spent working. That’s nearly one-fifth of your time.
How many full-time hours per year are there?
To calculate your annual work hours, you need to consider:
- Holidays
- Vacations
- Paid time off
Let’s say you had 12 vacation days and 8 paid days off last year. That’s 20 days or 160 hours off (20 × 8). Subtract that from 2,080 (the standard full-time hours), and you worked 1,920 hours in total.

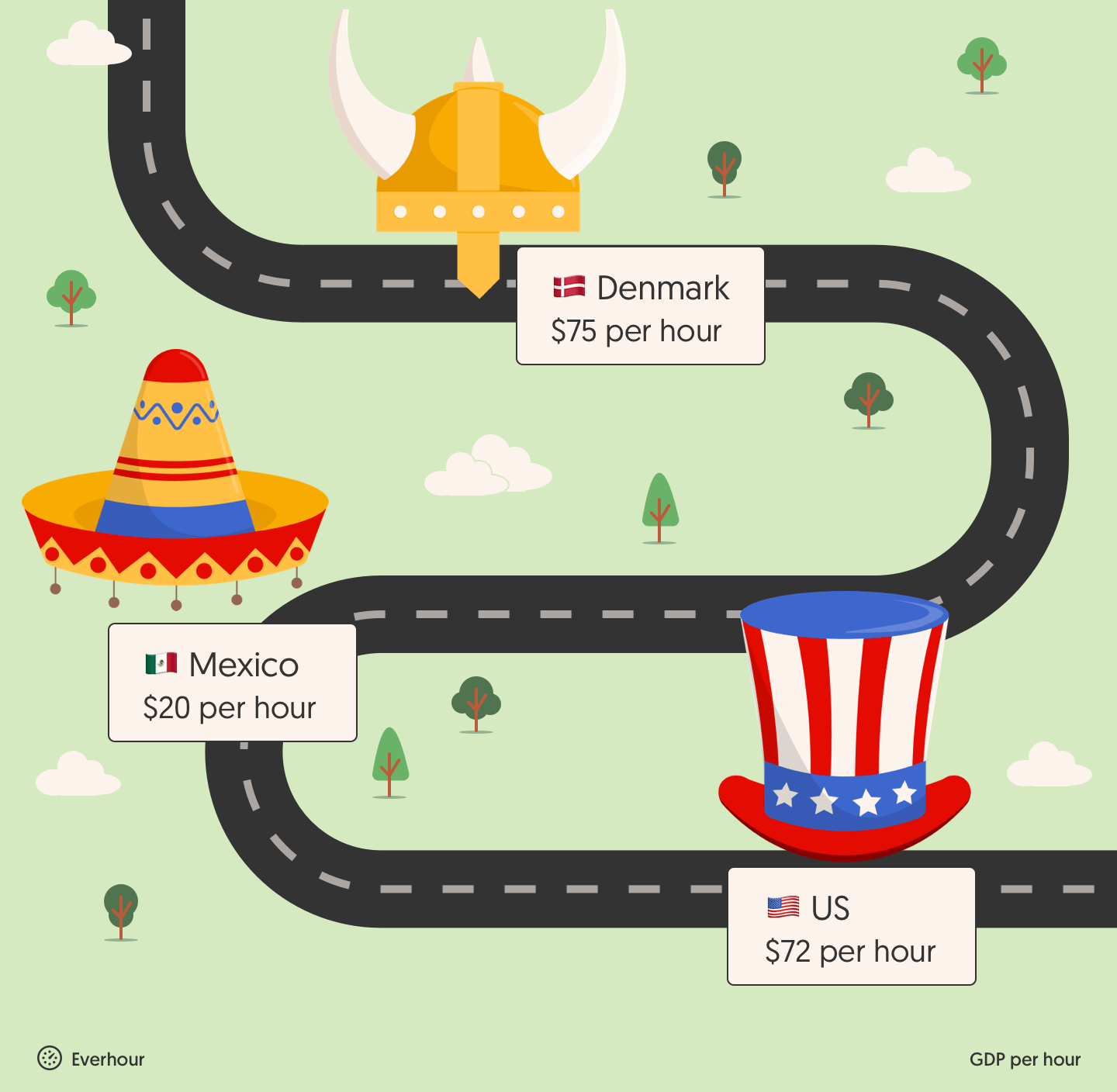
Work hours in a year: North America, Europe, and Asia
Work hours differ greatly depending on where you are. Here’s a snapshot:
Country with the longest working hours: 🇲🇽 Mexico – 2,137 hours/year
Country with the shortest working hours: 🇩🇰 Denmark – 1,380 hours/year
But here’s the twist: Danes earn $55 more per hour than Mexicans, showing that longer hours don’t equal higher productivity.
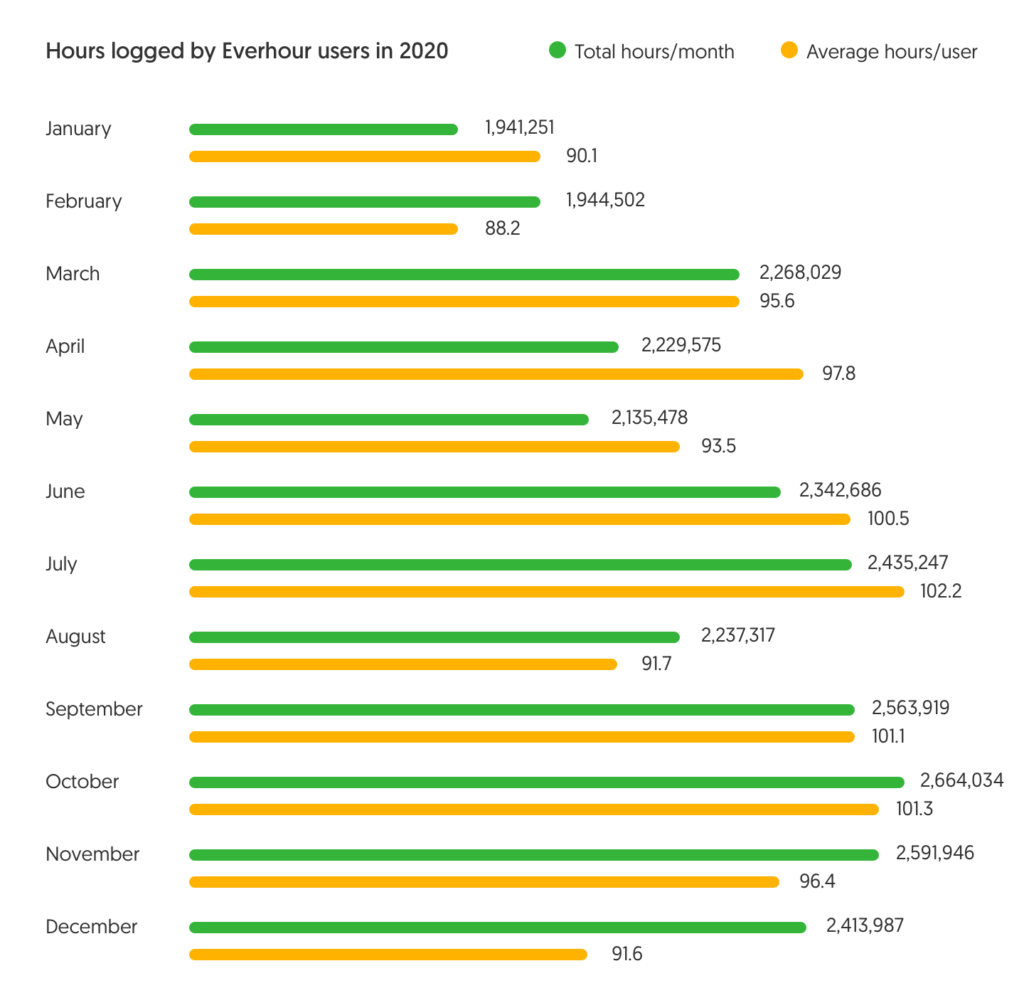
How many hours did Everhour users work last year?
Everhour users are a productive bunch. It’s a fact! But have you ever wondered about the average work hours in a year logged by Everhour users? Wonder no more! Here’s just how productive we’ve been together. *
*No GDPR was breached when making this infographic 😉
How many workweeks are there in a year?
There are 52 weeks in a year, but no one works all of them. Once you factor in weekends and holidays, that number drops.
To estimate how many weeks you actually work:
- Subtract holidays and weekends
- Divide the result by 7 (days per week)
But the question here isn’t always how many hours or weeks are worked in total. It’s also if an employee is receiving holiday pay. Normally, such holiday payments are included in contracts, so employees know if they are entitled to paid time off.
In the US, employers are not always required to compensate workers if federal holidays fall on a weekend. However, some companies choose to do so to gain loyalty and boost morale.
How many weeks in a year overall vs time spent working?
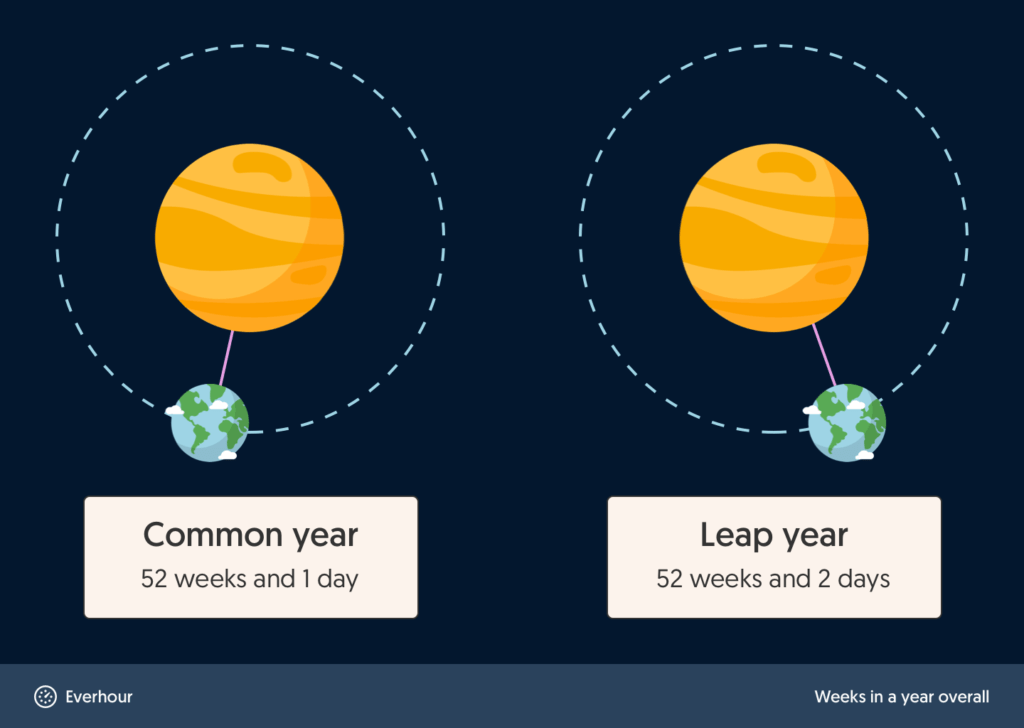
The International Organization for Standardization states that a year is 52 weeks. But if we want to get technical about it, it’s a little more than that. If you multiply 52 weeks by 7 days, you’ll get 364 days. But there are 365 days in a year, right? Correct!
That’s why there are 52.143 weeks in a year, or 52 weeks and one day. In a leap year, that becomes 52.286 weeks in a year or 52 weeks and two days. So:
1 Year = 52 weeks and 1 day
1 Leap Year = 52 weeks and 2 days
Now, how does this compare to time spent working? Let’s take a look at the weeks spent working by country:
Now, who is picking up their French textbook and booking a ticket?!
What do workweeks in a year look like worldwide? Fast facts!
Think it’s Monday to Friday everywhere? Think again. Workweeks vary around the world. Check out these fast facts:
- In many Muslim-majority countries, the workweek runs from Sunday to Thursday
- Mexico, Singapore, and Thailand (among others) have 6-day workweeks
- New Zealand and some Asian countries are trialing a 4-day workweek
- In Russia, Belarus, and other former Soviet Union countries, subbotniks (working Saturdays) are scattered throughout the year—citizens perform voluntary, unpaid work
How many workweeks in a year in North America, Europe & Asia?
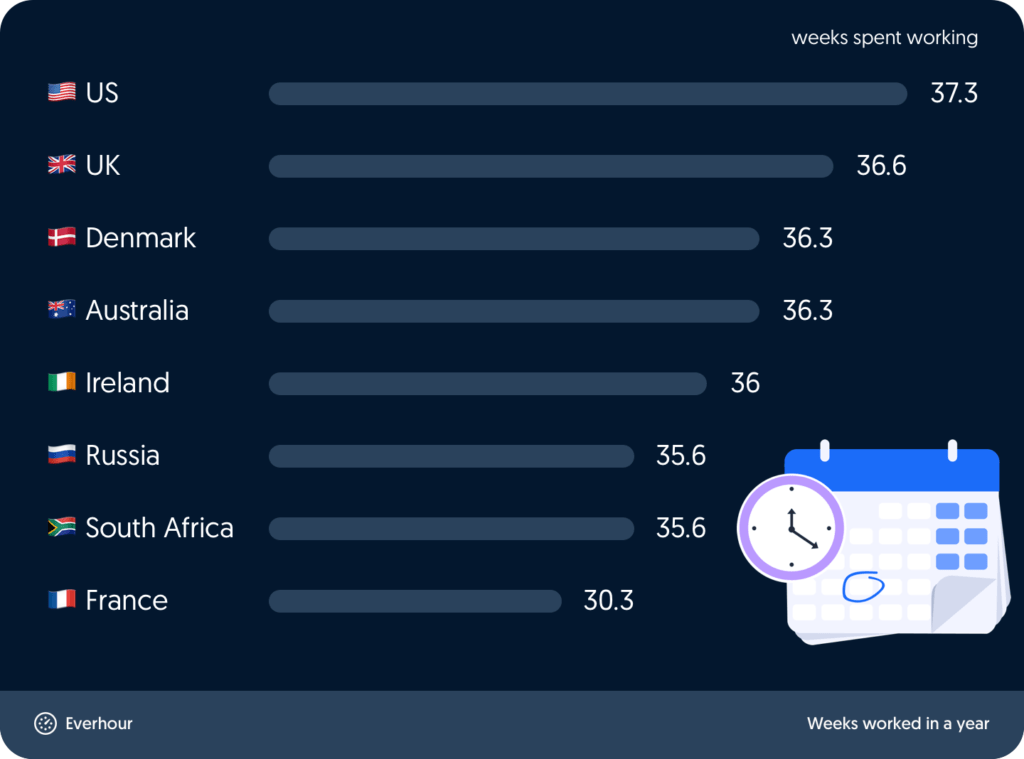
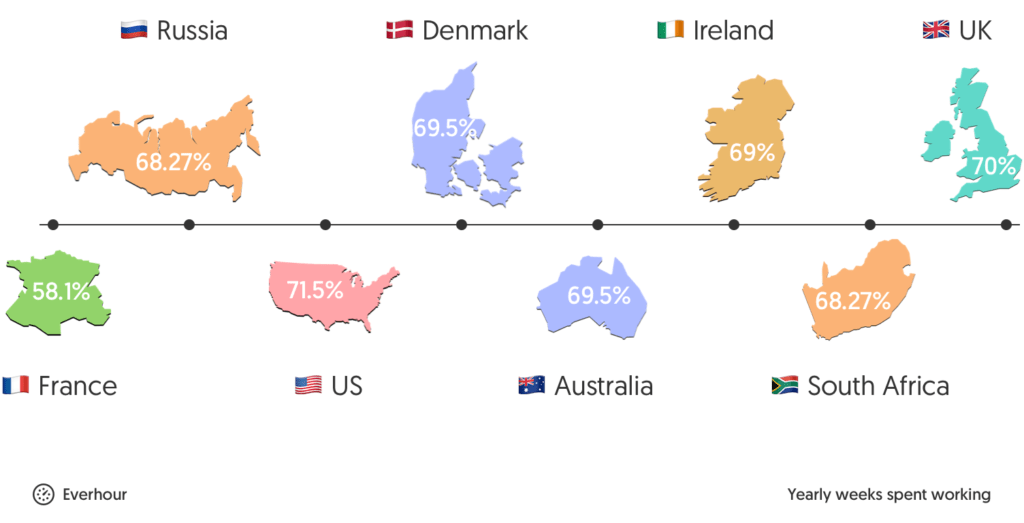
In theory, all 52 weeks of the year are available for work—but most people don’t work all of them. The average number of workweeks per year is around 36.3.
To calculate how many weeks you actually work, subtract holidays and weekends, then divide the remaining days by 7.
- UK: 256 working days = 36.6 workweeks
- US: 261 working days = 37.3 workweeks
- Denmark: 254 working days = 36.3 workweeks
- Australia: 254 working days = 36.3 workweeks
- Ireland: 252 working days = 36 workweeks
- Russia: 249 working days = 35.6 workweeks
- France: 212 working days = 30.3 workweeks
- South Africa: 249 working days = 35.6 workweeks
But it’s not just about how many weeks or hours are worked—it’s also about whether those holidays are paid. Typically, employment contracts spell this out.
In the US, employers aren’t required to compensate workers when federal holidays fall on weekends. However, some do so to boost morale and loyalty. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, as of 2019, about one-third of workers were eligible for 10 to 14 days of PTO after one year of service.
What Does the Average Working Month Look Like?
Whether you’re paid 4-weekly or monthly, you’ll probably want to know how many hours you’re getting paid for. Here’s how that time spent working compares to the rest of the world.
How many work hours in a month today vs 100 years ago?
Assuming a full-time role with a traditional schedule, calculating today’s work hours in a month generally looks like this:
40-hour workweek × 4 weeks = 160 hours per month
But that’s a rough estimate. Not every month has exactly four workweeks, and not everyone follows a 40-hour schedule. Some countries count workdays instead of full weeks. A more accurate way to calculate monthly work hours is:
40 hours/week × 52 weeks/year ÷ 12 months = 173.33 hours/month
Still, if we go with the rough 160-hour estimate, how does it compare to working hours a century ago?
In the early 1900s, amid industrial growth and global upheavals, work hours were significantly longer. In 1919, the average manufacturing workweek was about 50 hours, or roughly 200 hours per month. Over time, labor reforms helped reduce this. As of January 2023, the average workweek is 40.4 hours, translating to about 161.6 work hours per month.
How many hours in a month are there overall?
Thirty days has September, April, June, and November, all the rest have thirty-one, except for February. You may remember this rhyme from your schooldays, but it is still helpful when figuring out how many days and hours there are in a month.
So, let’s calculate:

Working 9 to 5? Here’s What the Average Working Week Looks Like Today
How many work hours are there in a week?
In 2024, full-time employees worked 42.9 hours per week (in the US).
How much time do we spend working on average?
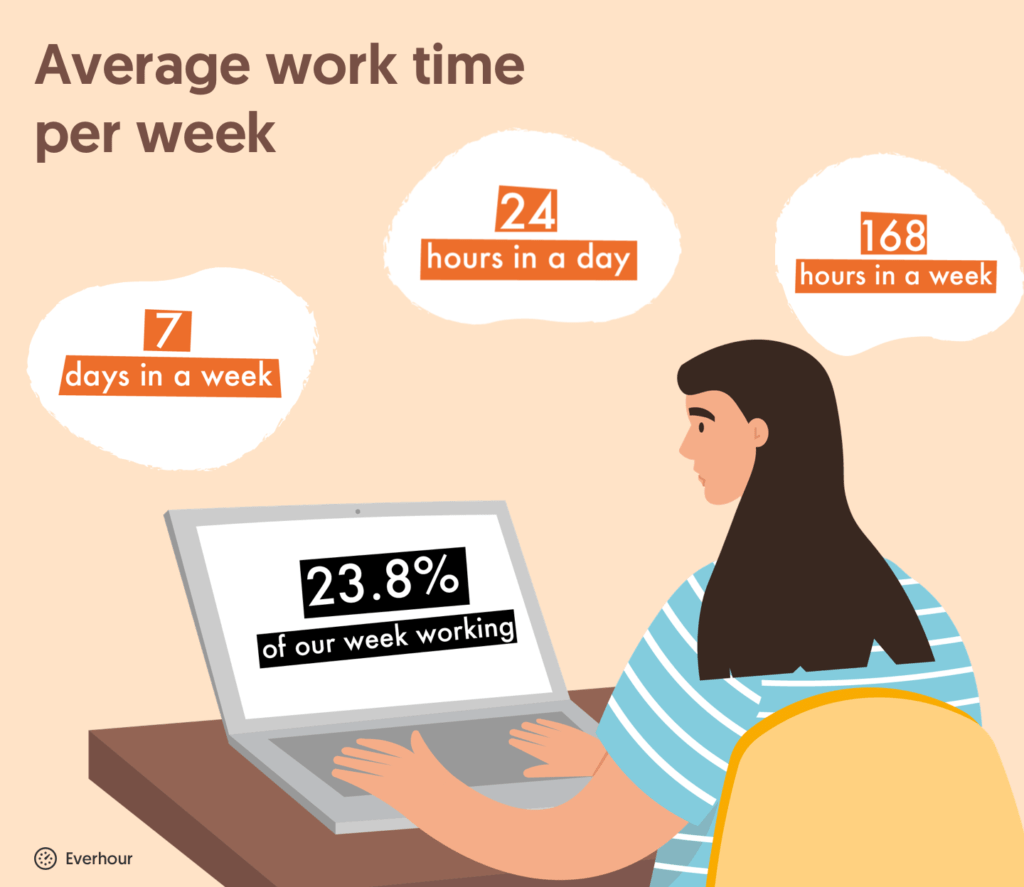
Ever wondered just how much of your week you spend working? Let us break it down for you with some handy math.
7 days in a week x 24 hours in a day = 168 hours in a week
So, if we take the average working week of 40 hours per week and make it a percentage we get:
23.8% of our week spent working
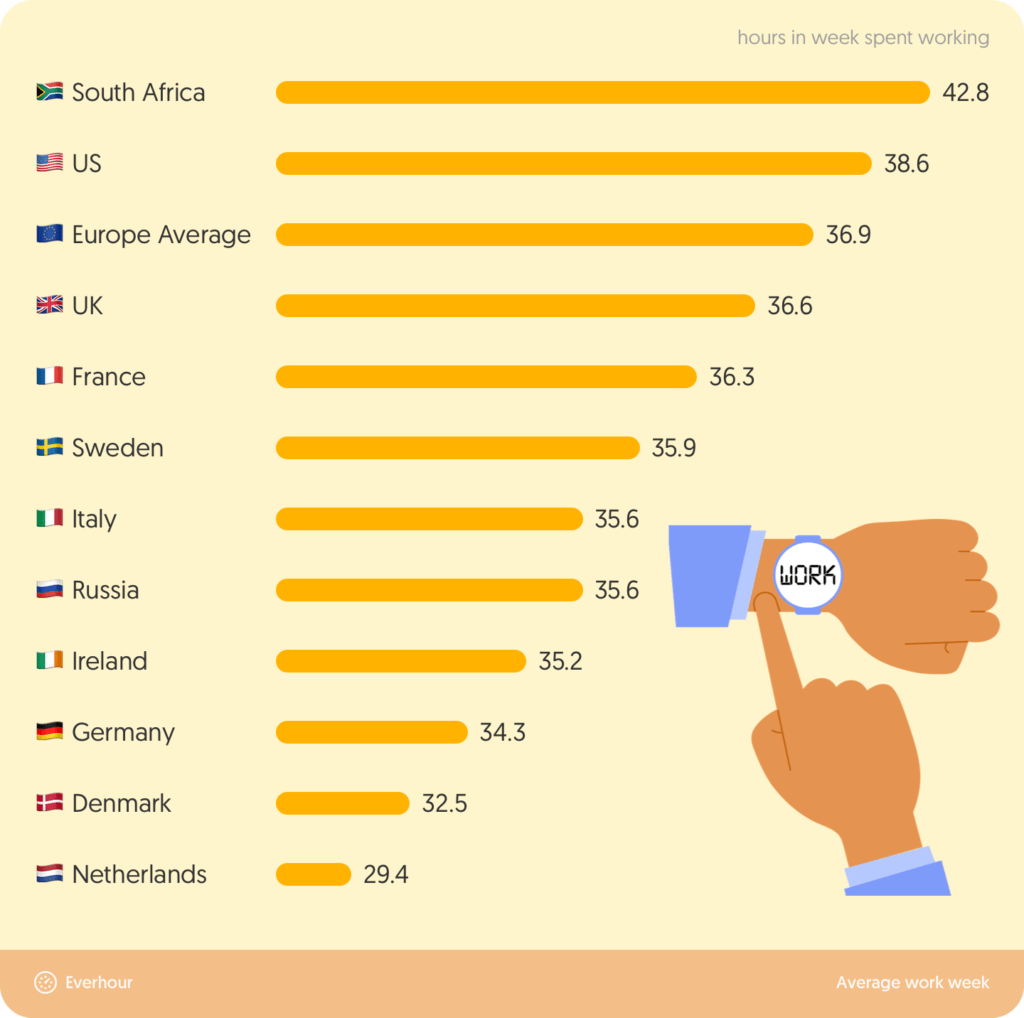
What is the average workweek in North America, Europe, and Asia?
We might have the impression that some nations are more laid-back than others, but is it really the case? Here are the true stats on the average working week in North America, Europe, and Asia. As you can see, the average work week hours in the US, for example, is under 40 hours.
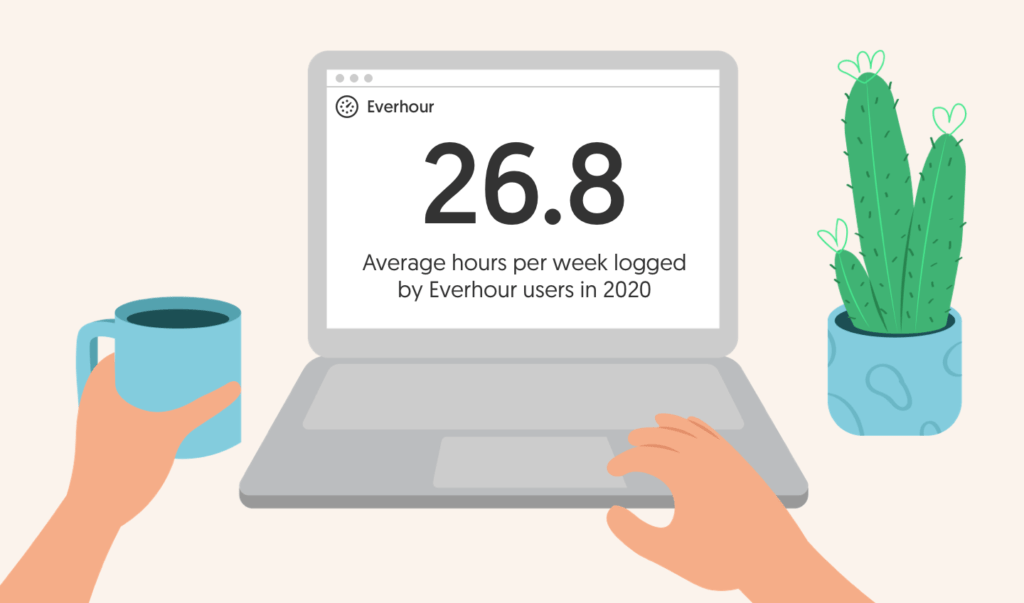
What are the average work hours per week as logged by Everhour users?
Hard workers or slackers (NO WAY!)? We know our Everhour users are some of the most efficient out there. But how many hours do they log each week? Let’s find out.
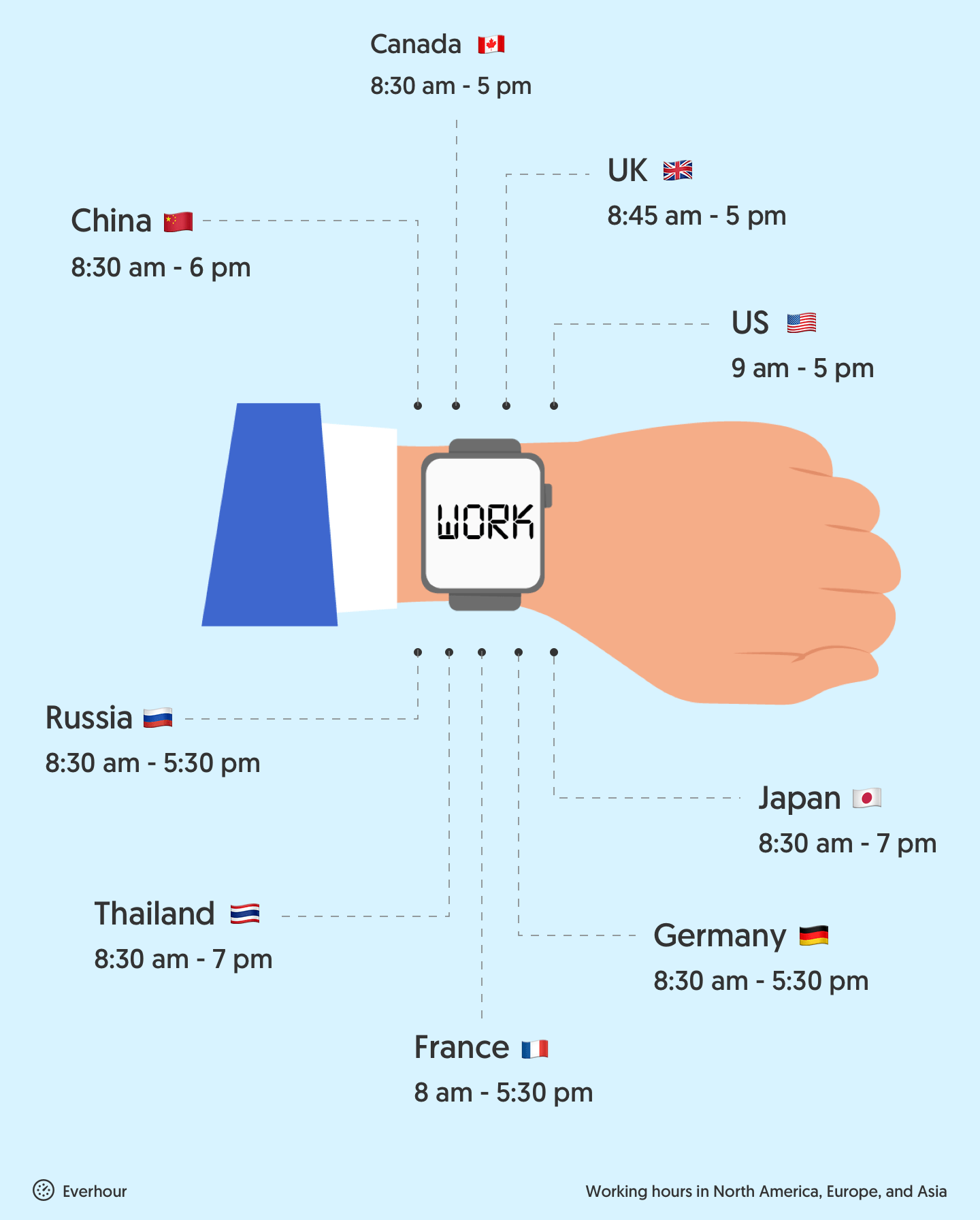
What are working hours in North America, Europe, and Asia?
We know the average working week across the world can range from 29 hours to well over 40 hours per week. But when do people work? Across the world, business days vary.
In the USA and much of Western Europe, the average working week is 9 am to 5 pm from Monday to Friday. Meanwhile, in Japan, the average business day runs from 8.30 am to 7 pm from Monday to Friday. However, in Saudi Arabia, the workweek starts on Sunday at 8 am. They work till noon, then take a 3-hour break before returning to work from 3 pm till 6 pm. Let’s take a look at some other daily routines around the world.
Who Works the Most? From Hong Kong to Washington
Discover which city and country work the most worldwide. And who has perfected the work-life balance?
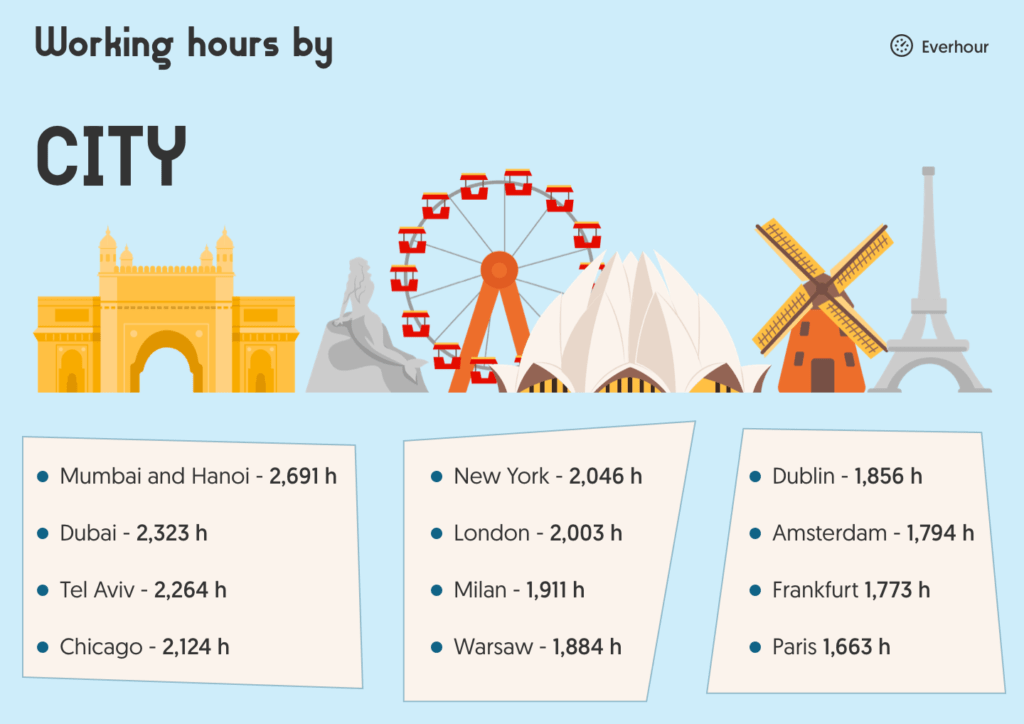
Which city works the most? Working hours by city
New York may be the city that never sleeps, and Melbourne the world’s most rested — but which city actually works the most?
Surprisingly, it’s not New York. In fact, it’s not even close. The title of the hardest-working cities goes to Mumbai (India) and Hanoi (Vietnam), both tied at the top with an astonishing 2,691 working hours per year.
On the other end of the spectrum, the city with the fewest working hours is Paris. Parisians average just 1,663 hours per year, making them the least-working city dwellers — and no, Melbourne doesn’t come in last.
Top 5 longest workers (hours per year)
- Mumbai and Hanoi 2,691 h
- Mexico City 2,622 h
- New Delhi 2,511 h
- Bogota 2,358 h
- Dubai 2,323 h
Top 5 shortest workers (hours per year)
- Paris 1,663 h
- Copenhagen 1,712 h
- Moscow 1,720 h
- Helsinki 1,750 h
- Frankfurt 1,773 h
Working Laws — How Many Hours Can a Young Person Work?
From getting their first paper round to that first “proper” job, it’s vital young workers receive the support and protection they need. Here are the rules employers need to know today.
How many hours can a minor work? Today vs 100 years ago
In the UK, child labor laws began with the Factory and Workshops Act, which banned children under 10 from working in factories or workshops. That was all the way back in 1878.
Before then, it was legal for kids, even under 10, to work in industrial settings. Just two years later, in 1880, the Education Act made school attendance compulsory. So, what was happening across the Atlantic?
In the United States, the turning point came in 1938 with the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). This law outlawed exploitative child labor and introduced strict rules for the employment of minors. But what did life look like before that?
A century ago, child labor was widespread. Kids as young as 10 — and sometimes as young as 5 — were expected to work. Not just helping around the house, but doing full labor in roles like:
- cotton picking and mill work
- factory jobs
- chimney sweeping
- retail work
- selling newspapers
- farming and more
Hard to imagine today, but this was once the norm. So, what changed? Society’s mindset and group norms.
Between 1908 and 1924, photographer Lewis Hine documented child labor across the U.S. for the National Child Labor Committee (NCLC). His photos exposed the harsh realities kids faced on the job.
Gradually, public opinion shifted. Wealthier families began to believe that children should be supported by parents, not be the providers.
By 1938, the FLSA became law, setting child labor limits that remain the foundation of youth employment regulation in the U.S. today.
What does the FLSA say exactly?
FLSA prohibits oppressive child labor and sets the following rules for non-exempt children, minimum age of:
- 18 years for hazardous occupations
- 16 years for employment in non-hazardous conditions
- 14 years for selected occupations – includes restrictions on hours and work conditions
Caught using oppressive child labor? The fine is $11,000 for every violation with up to $50,000 fine for death or serious injury of a minor. And this can be doubled for repeat offenders.
Think child labor is a thing of the past? It’s not! Since 2007, over 9,700 employers have been found guilty of violating these regulations – and that’s just the ones that were caught.

How many hours can a 17-year-old work in North America, Europe, and Asia?
| Region | Rules for 17-year-olds |
|---|---|
| USA |
Under the FLSA, 17-year-olds can work unlimited hours in non-hazardous conditions. States may impose extra restrictions:
|
| Canada |
17-year-olds can work similarly to adults, with exceptions:
|
| European Union |
Applies to youth aged 15–18 (no specific 17-year-old rules):
|
| Asia |
|
How many hours can a 16-year-old work in North America, Europe, and Asia?
| Region | Rules for 16-year-olds |
|---|---|
| USA | Like 17-year-olds, 16-year-olds can work an unlimited number of hours in non-hazardous conditions under federal law. |
| Canada |
16-year-olds are classified as “Young Persons” (15 to 17 years old). They can work from 6 am to 12:01 am, but:
|
| European Union |
Applies to 16-year-olds as part of youth labor regulations:
|
| Asia |
|
How many hours can a 15-year-old work in North America, Europe, and Asia?
In most countries, 15-year-olds are expected to attend school. So, this limits their labor activity. But by how much? How many hours can a 15-year-old work? Let’s find out.
| Region | Rules for 15-year-olds |
|---|---|
| USA |
Under federal law:
|
| Canada |
|
| European Union |
|
| Asia |
|
How many hours can a 14-year-old work in North America, Europe, and Asia?
Learning how to work is an important skill for any young person. But when getting started in the employment world, it’s vital that workers’ rights are protected. So, what are the rules of employment for a 14-year-old across the world?
| Region | Rules for 14-year-olds |
|---|---|
| USA |
Under the FLSA:
|
| Canada |
For ages 12 to 14:
|
| European Union |
|
| Asia |
|
How many hours can a minor work in a week in North America, Europe, and Asia?
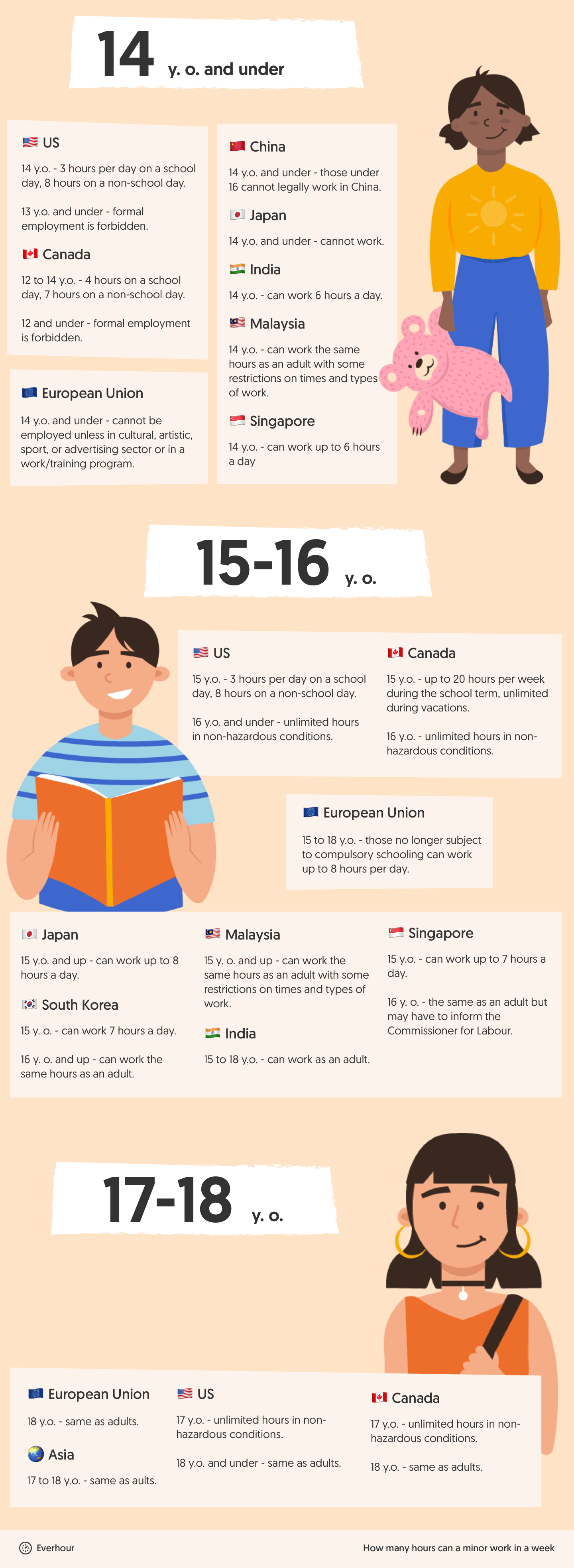
| Region | Age | Working rules |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 18 | Same as adults |
| 17 | Unlimited hours in non-hazardous jobs | |
| 16 | Unlimited hours in non-hazardous jobs | |
| 15 | 3 hrs/day on school days, 8 hrs on non-school days. Up to 18 hrs/week (term) or 40 hrs/week (vacation) | |
| 14 | Same as age 15 | |
| 13 & under | Formal employment forbidden | |
| Canada | 18 | Same as adults |
| 17 | Unlimited hours in non-hazardous jobs, between 6 am and 11 pm | |
| 16 | Unlimited hours in non-hazardous jobs, between 6 am and 12:01 am (9 pm–12:01 am supervised) | |
| 15 | Up to 20 hrs/week during school term, unlimited during vacations. Only between 6 am and 11 pm | |
| 12–14 | 4 hrs on school days, 7 hrs on non-school days, 20 hrs/week (term), up to 35 hrs (vacation) | |
| 12 & under | Formal employment forbidden | |
| European Union | 18 | Same as adults |
| 15–17 | Up to 8 hrs/day, 40 hrs/week if not subject to compulsory schooling. No work between 10 pm–6 am or 11 pm–7 am (varies by country) | |
| 14 & under | Only allowed in cultural, artistic, sport, or advertising work, or part of training/work experience | |
| Asia | China | Under 16 cannot legally work |
| India | 14-year-olds: up to 6 hrs/day. 15–18: can work as adults | |
| Japan | Under 15: cannot work. 15+: up to 8 hrs/day, 40 hrs/week with restrictions | |
| South Korea | 15: up to 7 hrs/day, 40 hrs/week. 16+: same as adults | |
| Malaysia | 14+: can work with restrictions on hours and type of work | |
| Singapore | 14: up to 6 hrs/day. 15: up to 7 hrs/day. 16+: same as adults but must inform Commissioner of Labor |
How Many Hours Can You Work on Unemployment in North America, Europe, and Asia?
Just because you are working doesn’t mean you aren’t eligible for unemployment benefits. Here’s the lowdown on how many hours you can work while claiming unemployment.
| Region | Policy |
|---|---|
| USA | Part-time workers may still be eligible for unemployment benefits (UI). Eligibility is based on gross wages, not hours worked. |
| Canada | Unemployed individuals may receive Employment Insurance (EI). You keep 50¢ of EI for every dollar earned, up to 90% of your weekly insurable earnings. |
| European Union (varies by country) |
|
| Japan | Part-time work is allowed while receiving benefits, but income must stay within the limits set by Japan’s Employment Insurance Law. |
How Many Hours Can You Work on SSI?
SSI (Supplemental Security Income) is a U.S. benefit designed to support individuals with limited income or resources, such as the elderly, blind, or disabled who are unable to work.
Key details about SSI:
- 👵🧑🦯 Eligibility: Available to aged, blind, and disabled individuals with little or no income.
- 💼 No work hour limits: You can work any number of hours but must stay within the income limits to receive benefits.
- 💵 Income limit: In 2020, income must be under $794 per month, with assets below $2,000.
- 📅 Benefit amount: In 2023, the maximum SSI benefit is $1,310 per month, based on your income level.
How many hours can you work if you are on disability?
Depending on where you are in the world, your eligibility for disability payments may vary. Here are some of the programs available worldwide.
| Country | Social Security Disability Benefits |
|---|---|
| USA |
|
| UK |
|
How Many Hours Can a Part-Time Employee Work Without Benefits?
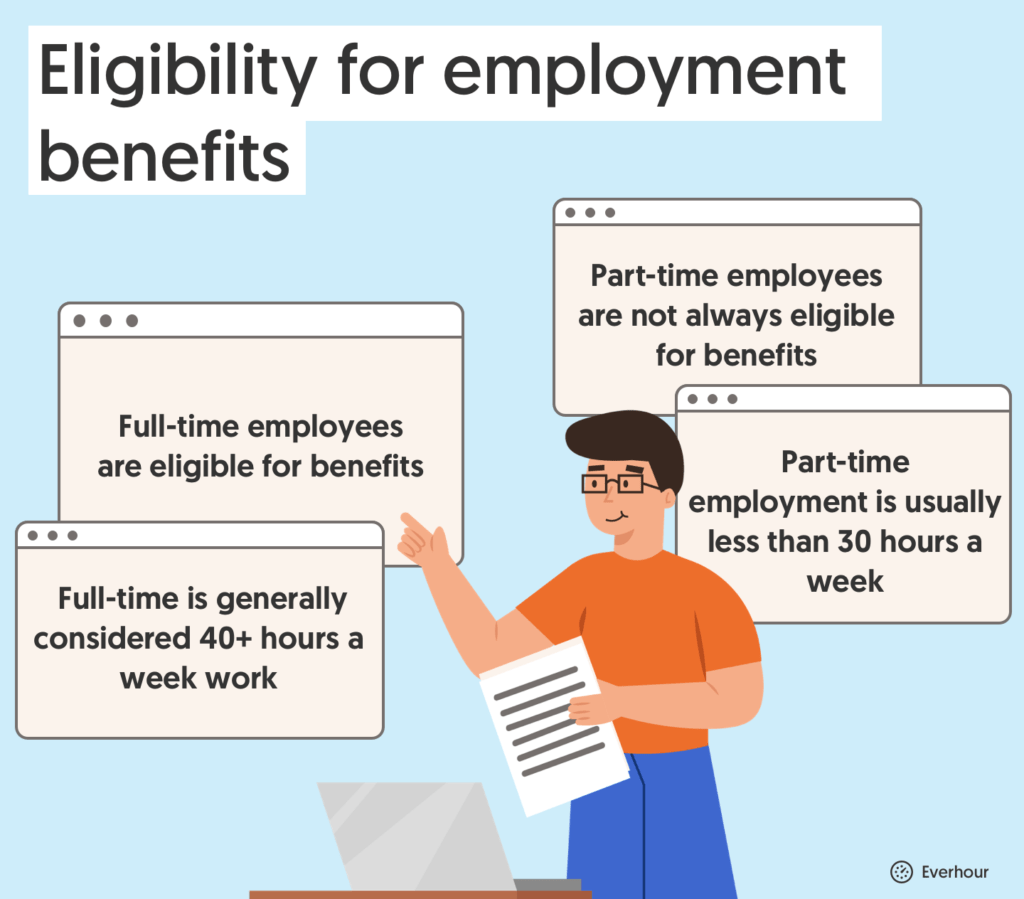
Eligibility for employment benefits, such as paid time off, stock options, health insurance, and more may depend on how your staff is classified.
- Full-time employees are eligible for benefits
- Part-time employees are not always eligible for benefits
- Full-time is generally considered 40+ hours a week work
- Part-time employment is usually less than 30 hours a week
BUT! It’s not that simple. Calculating whether you have a full-time or part-time worker should be done using data given by the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Should your employee receive benefits? If they are full-time – YES! If they are part-time, check your local laws. For example, in Hawaii, employees that work more than 20 hours per week are eligible.
In short, according to the Affordable Care Act, in 95% of cases, if your employee works more than 30 hours per week, they will be entitled to benefits.
How Many Hours Can You Work a Day in North America, Europe, and Asia? Maximum Working Hours per Day
There are 24 hours in a day, but how many of those can you actually spend working? Let’s break it down and explore the maximum working hours across different countries.
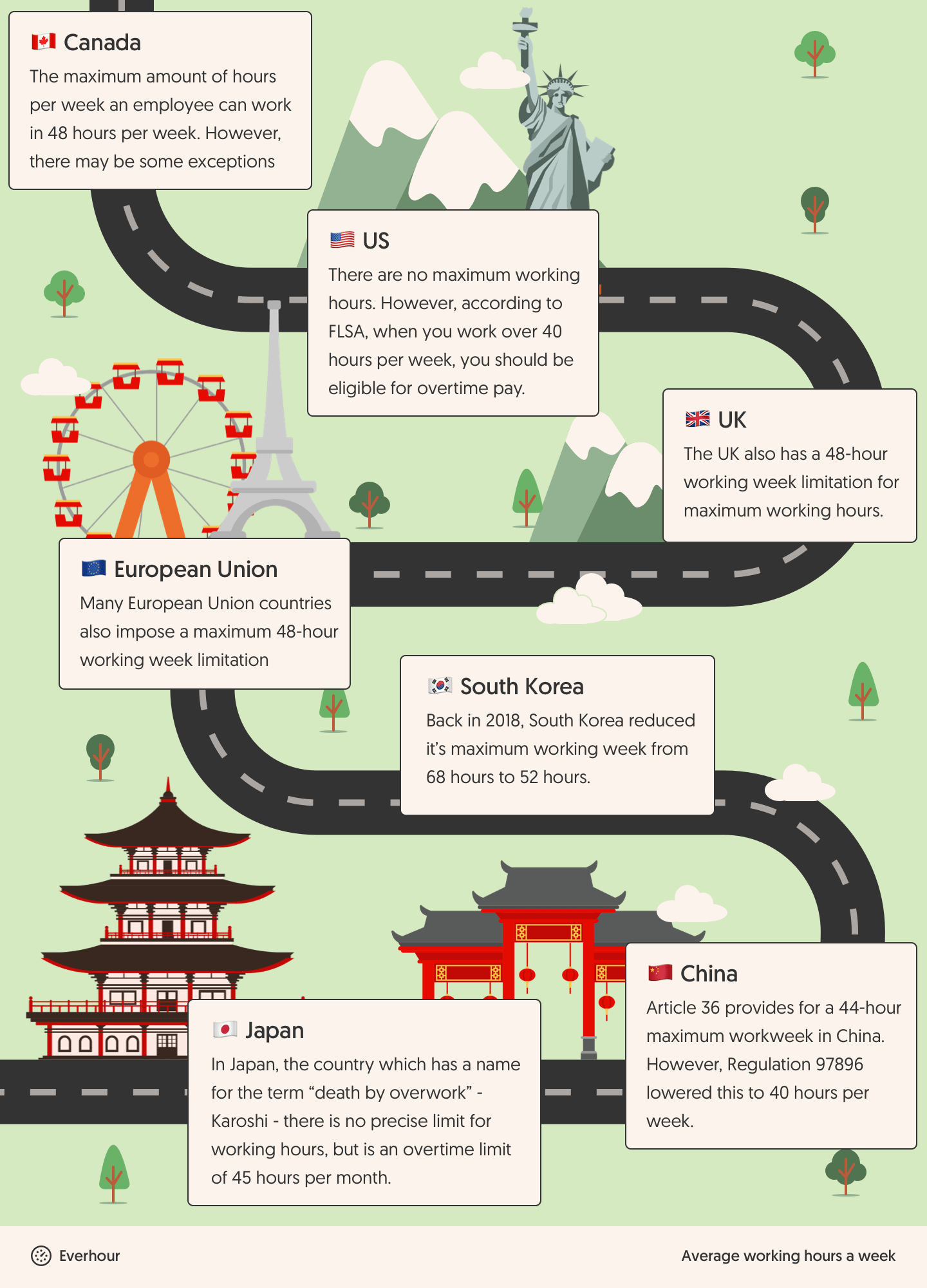
- USA: There’s no strict limit on working hours, but according to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), if you work more than 40 hours per week, you’re entitled to overtime pay.
- Canada: Employees can work up to 48 hours per week, though some exceptions may apply depending on the province and industry.
- European Union: Most EU countries have a maximum limit of 48 hours per workweek, in line with the EU working time directive.
- UK: The UK follows a similar 48-hour workweek limit as part of the European Union regulations.
- South Korea: In 2018, South Korea reduced its maximum working week from a staggering 68 hours to a more reasonable 52 hours.
- Japan: Known for its term “Karoshi” (death by overwork), Japan doesn’t have a specific workweek limit, but there’s a 45-hour overtime cap per month.
- China: While the Chinese Constitution originally set the workweek at 44 hours, Regulation 97896 further reduced it to 40 hours.
Average Working Hours: What’s Your Working Schedule?
Now you know more about the working world around you, why not get in touch and tell us more about how you work? Or better yet, let Everhour do the hard work of tracking your working time for you? We’re fanatics about time tracking, so we can tell you how many hours you and your team worked each day, week, month, and year, and see how you measure up in productivity with the world! Check out the best timers for work!
Resources:
- Child Labor Laws
- Employment Standards | Employment Standards | Young Employees
- Children and Youth at Work in India – Minimum Age for Work
- Youth Employment – Japan
- Malaysia Guide: Working in Malaysia, Hours, culture, working conditions: The Malaysian Employment Act defines
- Employment Standards – Hiring young people
- Japan tightens regulations on working hours and more
- Infographic: Who Works The Most Hours Every Year?
- What is the Average Hours Per Week Worked in the US?
- Hours worked – OECD Data
- GDP per hour worked – OECD Data
- Working Hours – Our World in Data
- Average usual weekly hours worked on the main job – OECD Stat
- Weekly average working hours – Statista
- Average weekly hours and overtime of all employees – US Department of Labour
- Why High Earners Work Longer Hours – National Bureau of Economic Research
- Trend in working hours – OECD Library
- List of minimum annual leave by country – Wikipedia
- Workweek and weekend – Wikipedia
- Full-Time Jobs With Shortest and Longest Hours – Monster
- Pre-industrial workers had a shorter workweek than today’s – MIT Edu
- Diminishing Returns at Work: The Consequences of Long Working Hours
- Are we working more than ever? – Our World in Data
- Average usual weekly hours worked on the main job – OECD Stat
- Hours worked – OECD Data
- Hours of work – annual statistics – Eurostat Statistics Explained
- Average weekly hours and overtime of all employees on private nonfarm payrolls by industry
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
- GDP per hour worked – OECD Data
- Comparative review of unemployment and employment insurance experiences in Asia and worldwide
- Who receives paid vacation leave?
- The Protection of Young Workers in Canadian Employment Law
- Teenage workers in the EU: Age limits & working time
- All our charts on Child Labor

