At first, understanding how to calculate the critical path, and how to use the critical path method in project management can seem daunting. To calculate the critical path effectively, you need precision and a keen eye for detail. But when you move past the concept of using a lot of data and algorithms to calculate it, you realize it’s pretty common sense!
In this article, we’ll take a dip into the critical path concept and its components, talk about why it’s a useful tool, and give you some critical path method examples, solutions for using project management software, the best time tracking software, and tools to aid you in calculating critical path.
Understanding the Critical Path in Project Management
In short, the definition of critical path is as follows:
The critical path is the longest sequence of activities in a project plan which must be completed on time for the project to complete on its due date.
Projects are broken into tasks, and the critical path is the series of tasks that takes the longest to complete the project, accounting for dependencies and other variables.
Simply put, the critical path determines the shortest possible project duration by lining up the longest sequence of dependent tasks.
Importance of the Critical Path Method
Big historical builds — like the Great Pyramid, the Great Wall, and the Panama Canal — didn’t happen by chance. They relied on early forms of project management, including what we now call the critical path method (CPM).
❗Why the critical path matters
Without CPM today, many projects would face:
- 🛑 Delays from hidden obstacles
- 🧩 Confusion over task dependencies
- 📉 Missed goals or failed launches
🧠 “The critical path is ‘critical’ because it’s the red alert path — miss a step or delay it, and your project won’t hit deadline.”
Success depends on following the right sequence and timing. And while there are other methods, CPM remains a go-to for planning complex, deadline-sensitive work.

Most Popular Project Managers Methodologies, Compared
See this post for a comparison of this and other popular project management methodologies!
Steps to Calculate the Critical Path for Efficient Planning
Before we dive in, for the visual learners among you, here’s a great, highly detailed video showing how to calculate the critical path:
Finding the critical path for a project rests first on six steps completed in order. Let’s break down those steps!
STEP 1. Divide the Project into Tasks
- Make a list of your tasks
- Assign each task with a name or a shortcode
STEP 2. Order and Identify Dependencies
- Put your tasks in a logical line-up
- Identify dependencies
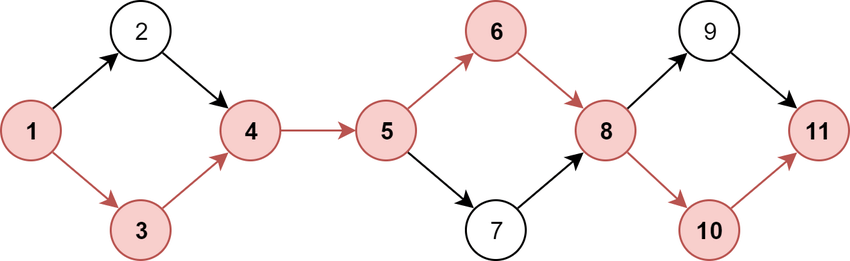
STEP 3. Create the Network Diagram
Now, you can make your task line-up visual. The good old pen-and-paper method may work well; a more sophisticated way of doing this is by using a network diagram such as a PERT or Gantt chart (more information to come on these later in this article) and connecting your tasks in the chart.
STEP 4. Estimate Duration
- Clearly define the beginning and end date for each task.
- Taking into account order and dependencies, set each task’s estimated duration.
STEP 5. Perform Resource Leveling
The main aim of resource leveling is to allocate resources efficiently so that the completion of a project lies within the given time, and no resource conflicts take place. Resource conflicts may lead to:
- Delays in the completion of specific tasks.
- Difficulties in assigning resources.
- Inability to change task dependencies.
- Removing tasks as needed.
- Adding more tasks as needed.
- Overall delays and budget overruns of projects.
STEP 6. Determine the Critical Path
Find the longest sequence of project tasks in the diagram. This sequence is the critical path for your project!
EDITOR’S NOTE 1:
There are usually three main types of anticipated dependencies in a project.
- Mandatory dependencies – dependencies due to the physical limitations of the task. Often, tasks in research and development projects are labeled as compulsory.
- Discretionary dependencies – dependencies due to decisions made by teams along the course of a project.
- External dependencies – dependencies due to a third party’s needs, e.g. needs of a contractor or shareholder.
EDITOR’S NOTE 2:
- To calculate the time for each task and prioritize them easily, use a time tracking app (like Everhour). This will help you to accurately monitor and evaluate time on your project.
- An app with time tracking capabilities can make leveling HR resources easier by allowing a team to more accurately predict future team efficiency based on past completion times, particularly in roles requiring specialization.
Variables Within Critical Path
Let’s take a look at some terms and concepts you’ll need to understand to be able to calculate the critical path.
Float/Slack
Float (sometimes called slack) of a task is the duration that it can be delayed without delaying the subsequent task, completing the project, or violating a schedule constraint.
Early Start and Early Finish
Early start (ES) and early finish (EF) are the earliest points a task can begin or end, assuming all prior tasks are completed as early as possible.
- 🔗 ES is only possible if the previous task ends on its EF.
- ⏳ EF = ES + task duration.
- 🧠 Starting early helps buffer time for riskier or unpredictable tasks later in the project.
👉 Forward Pass method of determining Early Start:
To determine early start and early finish, use the forward pass method:
- 🔍 Start with the project start date.
- ➡️ Move left to right through the network diagram.
- ⏱️ At each step, calculate the earliest possible start and finish based on the task before it.
👉 Steps to calculating Early Start dates:
- 📆 Take the early finish of the previous task as the early start of the current one.
- ➕ Add the current task’s duration to get its early finish.
- ⚙️ Factor in resources (e.g., staff availability, equipment, holidays).
- 🔄 Repeat for all tasks along the path to build the full schedule.
Late Start and Late Finish
Late start and late finish are the latest times a task can begin and end without delaying the project.
To figure them out, work backward from the final project deadline:
- 🔁 Start from the end of your project plan.
- ➡️ Move right to left through your network diagram.
- ➖ Subtract each task’s duration to find the latest it can start and still hit the final deadline.
📌 Remember: Just like calculating early start/finish, you still need to account for resource availability when doing the backward pass.
Best Tools for Calculating the Critical Path
Below, we’ll take a glance at some CP software, templates, and diagram generators available on the web to help get you started, stay organized, and be successful when determining the critical path for your project.
We’ll also get into how to use a PERT or Gantt chart to estimate critical path, and provide a clear, visualized model for the CP of your project.
Tools to calculate the critical path
You don’t need to build everything from scratch—these tools can help:
- 🔍 Search online: A quick Google search will lead you to critical path calculators and free templates.
- ⭐ Compare tools: Capterra lists top project management software with side-by-side comparisons, user ratings, and built-in Gantt chart tools.
- 🧩 Use MS Project: It comes with critical path calculators, Gantt generators, and tutorials. Learn more about using it here.
PERT chart for estimating the critical path
A PERT chart is a flowchart-style tool used to plan project timelines by outlining tasks and their sequences. It helps determine:
- how long each task will take
- which tasks can run in parallel
- which tasks depend on others
Key features of PERT:
- 🧮 Time estimates: Calculates the shortest, longest, and most likely duration for each task (try out bottom-up estimating)
- 🔄 Used during planning: Often applied in step 4 of the critical path method—estimating task durations
- 📈 Realistic planning: Preferred for its focus on practical completion times
- 🔢 Includes: float/slack time, early/late start and finish dates
📘 PERT chart terms to know:
- 🔵 Nodes: Circles representing tasks or milestones
- ➡️ Arrows: Show task order; can branch if tasks happen in parallel
- 🎯 PERT event: Marks the start or end of a task
- 🕒 Slack: How long a task can be delayed without affecting others
- 🚨 Critical path activity: Has no slack—delays here affect the whole project
- 🧭 Lead time: Time to finish a task without delaying the next one (see more)
Here’s a helpful video on how to create a PERT chart:
Gantt chart for estimating the critical path
Gantt charts work well for smaller projects by visually linking dependent tasks. In contrast, PERT charts are better suited for larger, more complex projects that involve mapping task networks.
Key differences and benefits of Gantt charts:
- 🔄 Used during the project: While PERT is for planning, Gantt helps track ongoing progress.
- ⏳ Shows task duration: Easily see how long each task should take.
- 👥 Highlights responsibility: Displays who is assigned to what.
- ⚠️ Exposes conflicts: Makes scheduling issues easy to spot.
- 🛠️ Editable timelines: You can update start and end dates as the project evolves.
To create a Gantt chart or bar chart, check out this video:
What’s the difference between a PERT and Gantt chart view?
Both Gantt and PERT charts help visualize a project’s tasks, timeline, and factors like resource use or task dependencies. But they differ in how they show that information:
🕸️ PERT chart: Uses a network or flow diagram
- Best for planning large or complex projects
- Highlights task dependencies and sequences
📅 Gantt chart: Uses a horizontal bar chart
- Ideal for tracking progress in smaller or ongoing projects
- Focuses on timelines and task durations
Critical Path Method: In Closing
Due to its incredible effectiveness, the critical path, along with a statement of work, is a project staple in organizations everywhere. We hope this article has helped make learning how to find critical paths much more straightforward. Happy planning!

