The week’s schedule is due, requests for time off are piling up, and your team is spread across weekends and multiple roles. A spreadsheet works until it doesn’t—miss one update, and suddenly shifts overlap or go unfilled. Many managers hit this wall and turn to scheduling software for help. In this guide, you’ll see how real teams move beyond Excel, which platforms they rely on most, and what features actually make scheduling easier. We’ll cover industry favorites like 7shifts, Homebase, HotSchedules, and Sling, along with pros and trade-offs you should know. You’ll also get tips for choosing a tool that fits your team size and industry, plus ways to streamline swaps, time-off requests, and compliance tracking. By the end, you’ll know how to schedule hourly workers and spend less time wrestling with schedules.
What Does “Scheduling Hourly Workers” Really Mean?
Scheduling hourly workers means turning business demand into shift coverage — matching the right people, with the right skills, at the right time. It balances availability, labor rules, and budgets. In short, it’s part math, part empathy, and part communication.
🎯 Core objectives
- ✅ Meet demand without under- or over-staffing
- 🕰️ Respect availability, time off, and labor rules (breaks, minors, overtime)
- 💸 Control costs (overtime, premium pay, last-minute changes)
- 🤝 Maintain fairness, predictability, and clear communication
- 📋 Record actual time worked to reconcile payroll and improve future schedules
📅 Common schedule patterns
- Fixed schedule — same days and hours weekly
- Rotating schedule — e.g., week A mornings, week B evenings
- Split shifts — two smaller shifts with a gap
- Compressed rotations — 4-on, 4-off for 24/7 coverage
- Seasonal/variable — workload surges during holidays or events
- On-call/standby — for unpredictable spikes or emergencies
- Self-scheduling — employees pick from approved open shifts within guardrails
Why it matters
- ⭐ Customer expectations are immediate — missed coverage hurts reviews fast
- ⚖️ Labor laws and fair workweek rules demand predictability and rest periods
- 🙌 Competitive hiring means predictable, flexible schedules boost retention
- 📊 Tight budgets make consistent scheduling essential to prevent overtime creep
Getting Started: Foundations Before You Schedule
Build these fundamentals once—you’ll reuse them every week.
🎯 Define coverage targets
Why it matters: Knowing peak hours prevents understaffing and overtime.
- Identify peak windows (sales, tickets, reservations, or task volume)
- Translate demand into labor with a simple formula:
Required labor hours per hour = Forecasted workload per hour × Average handling/processing time
Example: 60 orders per hour × 3 minutes each = 180 minutes (3 hours). If one person handles 60 minutes/hour → staff 3 people for that hour.
- Add a buffer (5–15%) for breaks, training, and variance
🧩 Map roles and skills
Why it matters: Matching people to tasks keeps operations smooth.
- Create a skills matrix (who can open, close, run register, supervise)
- Define critical coverage (must-have) vs. flexible coverage (nice-to-have)
- Spot cross-training opportunities to boost flexibility
📋 Establish scheduling policies
Why it matters: Clear rules reduce confusion and burnout.
- Posting timeline (e.g., publish 2 weeks in advance)
- Time-off request window (e.g., submit 14 days before schedule lock)
- Shift swap rules (self-service requests with manager approval)
- Maximum weekly hours or consecutive days to avoid overtime
- Rest periods & compliance guardrails (breaks, minors’ limits, local laws)
📅 Standardize schedule templates
Why it matters: Templates save time and keep coverage consistent.
- Baseline templates for weekdays, weekends, and events
- Save role-based patterns (e.g., “Open + Mid + Close”)
- Preload recurring tasks (inventory, cleaning, training)
🛠 Choose your tool
Why it matters: The right software reduces admin work and keeps everyone on track.
- Spreadsheets work, but apps cut admin time, enable self-service swaps, and layer forecasting & compliance alerts
- If your work includes project-based tasks, pair with time tracking (e.g., Everhour) to compare scheduled hours with actual effort and budgets
It’s everything your spreadsheet isn’t—and more.
Step-by-Step: How to Schedule Hourly Workers (Weekly Cycle)
Step 1: Forecast demand
- Pull last period’s actuals (sales, visitors, orders, tickets, calls).
- Adjust for promotions, reservations, weather, local events, or seasonality.
- Translate demand into labor per hour using your handling time and target service standards.
- Create a draft coverage chart (headcount by hour).
Step 2: Start from a template
- Load your closest-fit schedule template (weekday/weekend/holiday).
- Pre-populate fixed shifts (openers, closers, required supervisors).
- Layer in coverage for peaks; ensure breaks and turnover windows are visible.
Step 3: Apply availability and constraints
- Overlay employees’ stated availability and approved time-off.
- Honor legal constraints (minors, rest periods, max hours).
- Aim for fairness (rotate desirable and undesirable shifts and distribute weekends equitably).
Step 4: Fill open shifts and cross-check skills
- Assign by skill first (critical coverage roles).
- Prefer cross-trained staff for swing hours to absorb variance.
- Keep a small number of “flex” or “utility” shifts for the unknowns.
Step 5: Run a cost pass
- Estimate labor cost per day and per week (base pay × scheduled hours + expected premiums).
- Compare to your budget and adjust coverage at non-peak times first.
- Watch for overtime risks—rebalance before publishing.
Step 6: Publish early and clearly
- Share the schedule at least a week in advance when possible.
- Make every shift visible in the mobile app or shared channel; avoid sending screenshots that go stale.
- Highlight the deadline for shift swap requests and the final lock date.
Step 7: Manage changes with guardrails
- Allow self-service shift swaps with manager approval.
- Keep a “bench” list of part-timers willing to pick up extra hours.
- Document approvals in one system (not in scattered chats).
- If demand spikes, convert on-call or flex shifts into active shifts.
Step 8: Capture actuals and review
- Compare actual hours worked vs. scheduled.
- Note where breaks were missed, overtime appeared, or demand surprised you.
- In your next cycle, adjust templates and buffer levels accordingly.
Schedule Types: Pros, Cons, and When to Use Them
| Type | What it looks like | Best for | Watch-outs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed weekly schedule | Same days/times each week | Students, stable traffic, predictable roles | Less flexibility; may not fit seasonal peaks |
| Rotating schedule | Morning one week, evening the next | 24/7 operations or fairness rotation | Can disrupt personal routines; plan rest |
| Split shifts | Two smaller shifts in a day | Lunch/dinner peaks, delivery surges | Pay attention to split premiums (where required) |
| Compressed rotations (4–on, 4–off; DuPont) | Long shifts covering 24/7 | Security, manufacturing, healthcare | Fatigue risk; strict rest and break planning |
| Seasonal/variable | Larger rosters during holidays | Retail, hospitality | Ensure early posting to keep morale high |
| On-call/standby | Confirmed on short notice | Unpredictable demand | Comply with on-call pay rules where applicable |
| Self-scheduling | Staff pick open shifts within guardrails | Empowered teams; high morale | Requires clear rules to avoid gaps |
Manual vs. Software: What’s Right for You?
| Option | Strengths | Limitations | Best fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spreadsheet (manual) | Free, flexible, customizable | Error-prone, no alerts, slow change management | Very small teams with stable demand |
| Basic scheduling app | Templates, availability, swaps, reminders | Limited forecasting or analytics | Small to mid-size teams needing less admin |
| Advanced WFM | Forecasting, compliance, multi-location roll-ups | Higher cost/complexity | 24/7 ops, multi-site, heavy compliance |
How to Schedule Hourly Workers: Everhour Fits Into Hourly Scheduling Workflows
Shifts by Everhour helps managers plan and communicate work schedules clearly—showing who works when and where, while keeping coverage, costs, and compliance in check. If your business runs on hourly staffing—like retail, hospitality, support, or field operations—Shifts makes scheduling fast, transparent, and easy to adjust when plans change.
Where Shifts by Everhour adds value
- Smart scheduling: Drag and drop weekly or monthly shifts, assign by role or skill, and duplicate templates for recurring patterns.
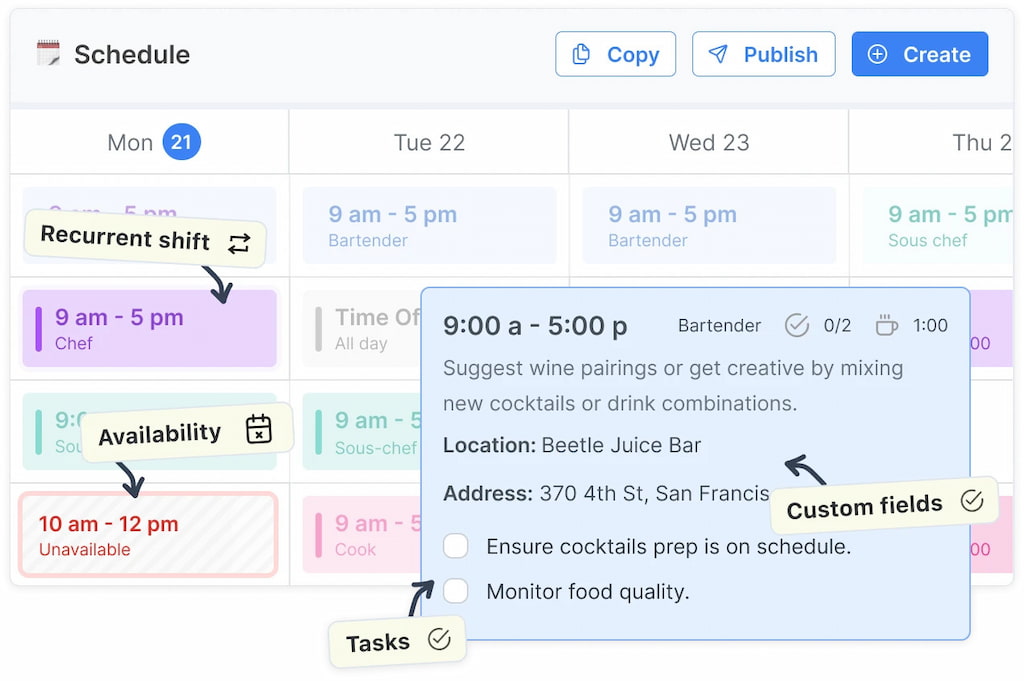
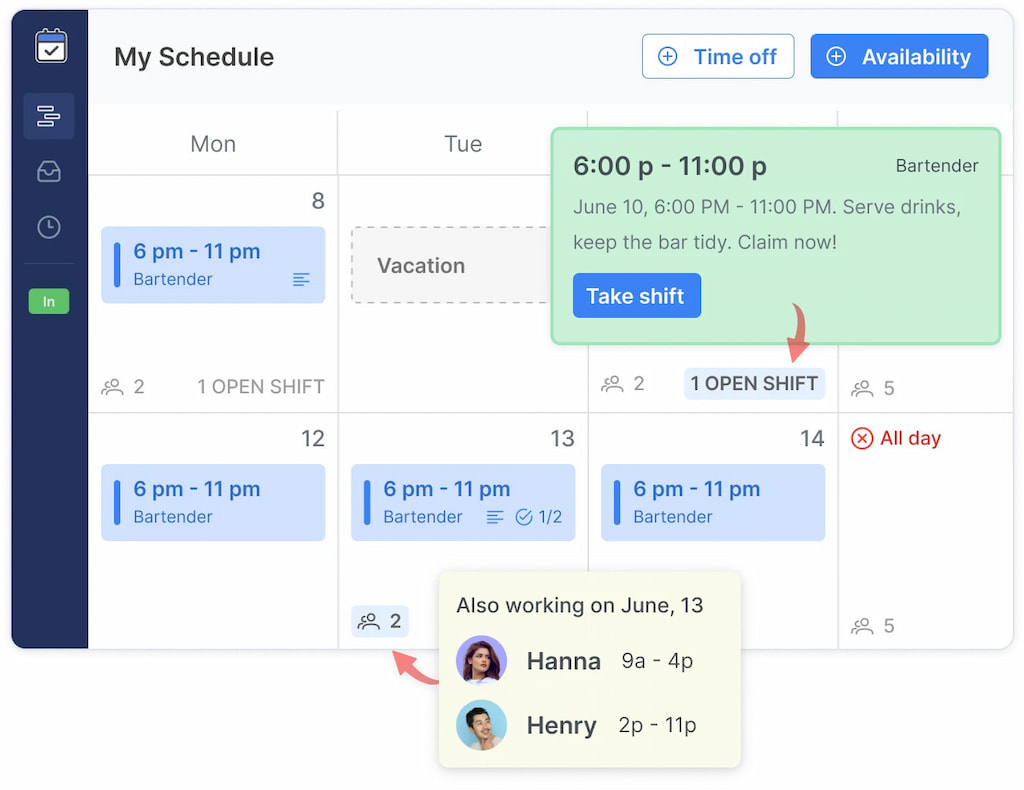
- Real-time visibility: Employees get instant notifications when shifts are published, changed, or swapped—no spreadsheets or scattered messages.
- Shift swaps & approvals: Team members can request swaps while managers keep control over final approvals.
- Labor cost control: Track scheduled hours and estimated wages per day or week to stay within budget.
- Compliance made easy: Alerts help you respect breaks, rest periods, and labor laws.
- Availability & time-off integration: See who’s available, approved for leave, or near overtime before assigning shifts.
- Integrated time tracking: Connect with Everhour to log actual hours worked, compare scheduled vs. real time, and feed payroll automatically.
- Multi-location coordination: Manage multiple sites or departments from a single dashboard for full visibility.
A simple workflow example
- Create your weekly schedule in Shifts by Everhour, using templates or drag-and-drop scheduling.
- Publish the schedule so employees receive instant notifications via web or mobile.
- Track attendance as employees clock in and out directly from Shifts.
- Monitor changes—approve swaps, handle call-outs, and reassign shifts without losing visibility.
- Review and export data for payroll, budgeting, or future planning.
Tips & Best Practices: The Habits That Keep Schedules Calm
🕒 Publish early, change less
- Publish at least one week in advance; two weeks is even better.
- Set a clear swap/request cutoff and hold the line unless coverage is at risk.
⚖️ Make fairness visible
- Rotate premium shifts (open/close, weekends, holidays).
- Share a transparent allocation policy (seniority, points, rotation).
⏱️ Guard against overtime creep
- Cap weekly hours for non-supervisors unless explicitly approved.
- Use alerts for early clock-ins and long closes.
- Train shift leads to release staff when coverage exceeds live demand.
🍎 Plan breaks realistically
- Schedule breaks explicitly; don’t rely on “fit them in.”
- Use floaters or flex roles to keep service steady during breaks.
💪 Build a bench and cross-train
- Keep a short list of trained part-timers for extra coverage.
- Cross-train employees so one absence doesn’t derail operations.
🔄 Use self-service with rules
- Allow swap requests inside the scheduling app.
- Require manager approval and a time-bound cutoff (e.g., 24 hours prior).
- Disallow off-the-books swaps; the published schedule is the source of truth.
🔮 Forecast the easy way
- Reuse last year’s like-for-like weeks and adjust for promotions/events.
- Track a baseline variance buffer (5–15%) and tune monthly.
- Log surprises (weather spikes, town events) to improve future forecasts.
💤 Respect rest and predictability
- Follow rest-period rules between close and open shifts.
- Avoid frequent last-minute postings; predictability improves retention.
📝 Document, don’t DM
- Keep approvals and notes inside your scheduling system.
- Group chat is fine for culture—not for official shift changes.
How to Handle Common Scheduling Challenges
📞 Last-minute call-outs
- Maintain a priority bench list (cross-trained, opted-in staff).
- Offer the shift through the app, approve on a first-come, skill-appropriate basis.
- Document replacements in the schedule, not in text threads.
📆 Uneven weekend loads
- Rotate weekends on a fair cadence or use a preference bidding system.
- Offer premium shifts occasionally to offload less desirable slots.
🎓 Students or second-jobbers with narrow availability
- Gather availability at the same time each semester/season.
- Use micro-shifts (3–4 hour blocks) where legal and useful.
- Post schedules early so they can coordinate around classes or other jobs.
🌱 Seasonal peaks
- Publish seasonal templates two months in advance.
- Hire and train seasonal staff with shadow shifts built in.
- Add Shifts by Everhour budgets for seasonal projects to understand true labor needs.
🌍 Multi-location coverage
- Dedicate a few floating employees who can cover nearby sites.
- Keep consistent role names and pay bands to simplify cross-location swaps.
- Standardize templates but allow location-level tweaks.
Compliance and Legal Guardrails (Non-Legal Guidance)
- Breaks and meals: Put them on the schedule; enforce and document.
- Overtime: Track scheduled vs. actual and rebalance midweek.
- Predictive scheduling (where applicable): Post within required timelines and compensate for last-minute changes per local law.
- Minors: Obey hour and time-of-day restrictions; hard-code guardrails in your system.
- Premiums (split shifts, late notices): Budget and apply consistently.
A Lightweight Staffing Math Primer
-
Translating demand to headcount
Formula: Required headcount per hour = (Workload per hour × Average handling time in minutes) ÷ 60
Round up, then add a buffer for breaks and variance. -
Planning breaks
Formula: Break coverage = (Number of staff × break minutes per shift) ÷ operating minutes
Example: If you need 2 people on register at all times and each must take a 30-minute break, ensure a floater or staggered coverage prevents dips. -
Budget sanity check
Formula: Weekly labor cost = Σ (scheduled hours × base pay) + expected premiums
Compare against your target labor % (e.g., labor cost as a percentage of revenue). If it’s high, cut low-impact hours, not peak coverage.
Clean Comparison Table: Ways to Coordinate Swaps and Changes
| Method | Pros | Cons | Recommended use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open shift board | High transparency; fast fills | Risk of underskilled picks without rules | With skill guardrails and approval |
| Direct manager assignment | Control and quality | Manager time burden | Emergencies or critical roles |
| Self-swap with approval | Empowering; less admin | Needs clear cutoff and skill checks | Day-to-day changes within policy |
| Group chat | Fast in a pinch | Creates confusion; no audit trail | Avoid for official changes |
FAQs: How to Schedule Hourly Workers Without Spreadsheets
How far in advance should I publish schedules?
As early as your business allows. One week is a solid baseline; two weeks is ideal for predictability and retention. If you’re in a fair workweek jurisdiction, follow the required posting window.
What’s the simplest way to estimate coverage?
Use last period’s actuals and a handling time estimate. Then convert to required labor hours and add a buffer (5–15%). Track the difference between scheduled and actual weekly, and tune your buffer.
How do I prevent overtime without short staffing?
Cap hours per person, prioritize coverage during peaks, and rebalance midweek if early demand was lower. Use alerts for early clock-ins and approvals for extended closes.
Should I allow employees to swap shifts?
Yes—with rules. Let the scheduling app handle requests and approvals so coverage and skill requirements stay intact. Avoid off-platform swaps.
How do I schedule minors?
Follow local restrictions on hours, time of day, and consecutive days. Bake guardrails into your schedule templates and approval workflows.
What if we run project work alongside shifts?
Layer time tracking with Everhour. Create projects (e.g., “Holiday Reset,” “Store Remodel”), set budgets, and compare task-level actuals with scheduled shift hours to plan smarter next time.
Do I need a scheduling app, or can I stick to spreadsheets?
Spreadsheets work for very small, stable teams. If you’re handling frequent changes, multiple roles or locations, or compliance alerts, a scheduling app pays for itself in time saved.
How do I make schedules feel fair?
Rotate weekends and premium shifts, distribute closings and openings evenly, and be transparent about the rules. Consider a preference survey each quarter to balance fairness with availability.
Final Thoughts: How to Schedule Hourly Workers
Scheduling hourly workers isn’t a template you set once; it’s a weekly operating rhythm. When you forecast demand, publish early, set clear swap rules, and capture actuals, you build a calmer system that protects both service quality and your team’s well-being.
Use templates for speed, guardrails for fairness and compliance, and a small buffer for real life. If your operation mixes shift work with projects or client deliverables, add Everhour to see how scheduled hours translate into task-level effort and budgets. Small improvements—posted earlier, swapped within rules, breaks planned on paper—compound into fewer surprises, smarter labor spend, and a team that trusts the process.
The goal isn’t a “perfect” schedule—it’s a reliable, adaptable one that your people can live with and your customers can feel in every interaction.
- Learn why manual scheduling costs your business a lot and how a shift scheduling tool will fix that!
- Discover how to make a work schedule for employees free and streamline your planning without paying a cent.

